Free Aerospace CNC Machinist course (6 month)
Aerospace CNC Machinist:
Brief Job Description: This role primarily involves CNC machining of aerospace components/ structures in all pre-machining & post machining stages alongwith self inspection & gauging.
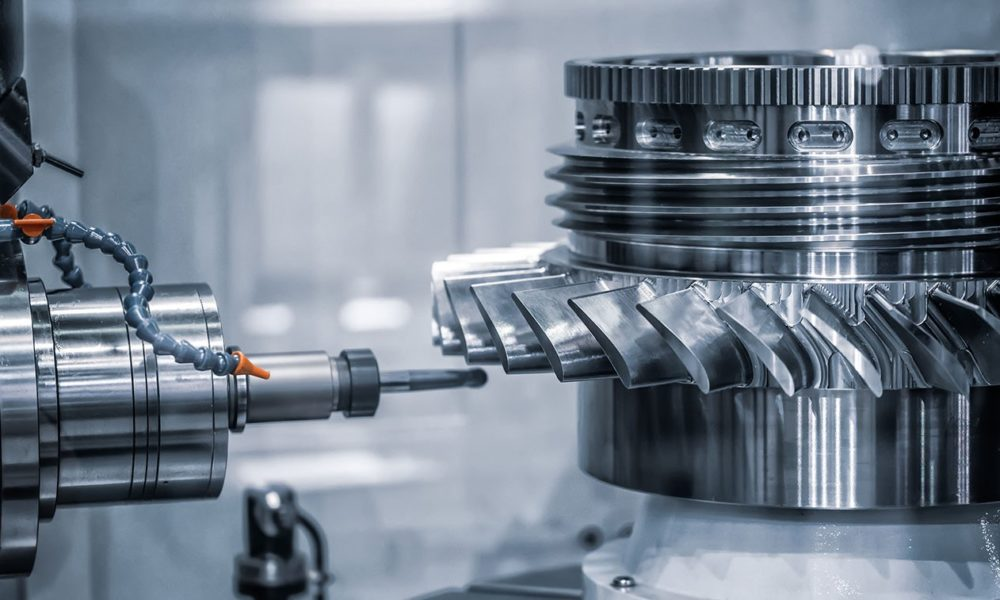
Personal Attributes: The individual should have basic communication ability and should be responsible in order to maintain procedures. He should have the ability to understand engineering drawings, do’s and don’ts of manufacturing process defined in work instruction or by a shop supervisor.
Pre-machining activities :-
Performance Criteria:-
Collect manufacturing drawing and process requirements
PC1. obtain drawings, route card / work instruction / CNC process sheet / CNC set-up sheet, details of fixtures (if any) from shop supervisor
PC2. check right Computer Numerically Controlled (CNC) programme and right tools required for machining of aerospace components
PC3. draw the raw-material as per specification
PC4. check for satisfactory functioning and calibration of the machine
PC5. plan the machining process as per process sheet or route card.

Prepare tools, arrange jigs and fixture
PC6. arrange the required tool from stores
PC7. arrange appropriate jigs and fixtures as mentioned in the manufacturing drawings / route card / setup sheet / process sheet
PC8. establish machine datum reference after following proper procedures as per CNC set up sheet
PC9. check output requirements/ limits of machining e.g. surface finish, specific orientation, gauge inspection etc.
PC10. understand any other specific requirement for machining from process sheet/ route card or work instruction and grain direction,if any.

Pre-machining readiness–
PC11. ensure that do’s and don’ts provided in the work instruction is adhered
PC12. trial run the CNC programme if specified by the CNC programmer or provided route card / work instruction
PC13. discuss technical matters related to machine programming with the engineer/ supervisor.

Knowledge and Understanding–
Organisational Context
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand:
KA1. relevant standards and procedures followed in the company
KA2. different types of products manufactured by the company
KA3. different types of machining processes/ tools available
Technical Knowledge
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand:
KB1. aerospace manufacturing standard and procedures such as ISO 9001, AS9100, etc
KB2. different types of machining processes
KB3. basic fundamentals of machines and mechanics
KB4. different types of tools used in the machining process with respect to type of process to be conducted
KB5. basic principles of 5S in manufacturing
KB6. application of coolant and lubricants
KB7. impact of various machining processes on the final product outcome
KB8. basic arithmetic and calculation methods for tolerance limits
KB9. safety guidelines related to different machines.
Skills

Core Skills/ Generic Skills
| Writing skills |
| The user/ individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SA1. write basic level notes and observations SA2. draw basic level geometrical/ mechanical drawings and charts |
| Reading skills |
| The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SA3. read and interpret workplace related documentation SA4. read and interpret engineering drawings and sketches to understand the dimension of the output product |
| Oral Communication (Listening and Speaking skills) SA5. discuss task lists and job requirements with co-workers SA6. effectively communicate information to team members SA7. discuss with supervisor in order to understand the nature of the problem SA8. attentively listen with full attention and comprehend the information given by the speaker Professional Skills SB1. judge when to ask for help from a supervisor SB2. suggest options to operators in case any issue is observed during operations Plan and Organise The user/ individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SB3. plan work assigned on a daily basis and provide estimates of time required for each piece of work SB4. prioritise actions to achieve required outcomes Customer centricity: The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SB5. ensure that customer needs are assessed and every effort is made to provide satisfactory service. Problem solving: The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SB6. recognise a work place problem or a potential problem and take action SB7. determine problems needing priority action SB8. gather information and provide assistance as required to solve problem SB9. refer problems outside area of responsibility to approach Analytical thinking The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SB5. analyse the complexity of work to determine if it can be successfully carried out SB6. ability to visualise the final product from the engineering drawing/ machine drawing, sketch provided by the supervisor SB7. analyse the cause of defects related to e.g. cutting tools, machine, fixtures etc. Desire to learn and take initiatives SB8. learn from mistakes by analysing and discussing with peers/ seniors SB9. discuss new ideas and participate in new initiatives SB10. follow instructions and work on areas of improvement identified SB11. complete the assigned tasks with minimum supervision SB12. complete the job defined by the supervisor within the timelines and quality norms. Critical Thinking Skills The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SB13. concentrate on task at hand and complete it without errors SB14. apply balanced judgments to different situations. Perform machining operations:- Performance Criteria– Set up a job / work-piece on the machine To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to: PC1. check the drawing issue (in route/ book card) and ensure that the latest issue/ version is being used PC2. check the calibration certificate of machines before using the same PC3. study the CNC set-up sheet , drawing, route-card of the component to be machined. PC4. obtain the relevant cutting tools from the tool crib and verify the same. PC5. identify the right raw material of given size, specification and verify the same PC6. change the cutting tool of the CNC machining centre as per the process requirement PC7. set up and adjust machine tools, fixtures/ jigs and cutting tools in order to perform machining operations and keep dimensions within the tolerance limit specified in the Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)/operating manuals/ route card / process sheet PC8. lift the work piece/ metal stock manually or through a hoist and position the same securely in the machine using fasteners and hand tools and verify their positions with measuring instruments PC9. load the component and check the centering and facing of the work pieces and check for alignment of the work pieces as per the final product output specifications. Transfering relevant CNC programmnes to the machine system and perform machining on the component as per route card / process sheet:- PC10. start the macine for operations and select the right cutting tool as per tooling instructions and as per the supervisor’s instructions PC11. understanding of the metallurgical properties of the machined parts PC12. check the surface of the work-piece to identify any abrasions, holes, inclination etc PC13. ensure that the right command is entered in the CNC machine as per defined machining parameters PC14. ensure that cutting tool length is as per process sheet so that is does not cause deflection in the cutting tool PC15. run right CNC programme for type of component to be machined PC16. turn on the coolant valves to maintain temperature in the machine chamber, wherever necessary PC17. brush or spray lubricating material on work pieces where applicable PC18. take appropriate action in case of any irregularities e.g. power failure, rejection, tool breakage etc. Collection of requisite machine tools from tool crib:- PC20. ensure tool replacement as per recommended tool life PC21. enter readings of key dimensions on control charts/ record; provide required tool offsetting with the help of supervisor. Knowledge and Understanding:- Organisational Context The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand: KA1. relevant standards and procedures followed in the company KA2. different types of products manufactured by the company KA3. different types of machining processes/ tool available KA4. process flow/ routing of various components in the machine shop/ organisation Technical Knowledge The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand: KB1. different types of machining processes KB2. different types of tools used in the machining process and their identification KB3. basic fundamentals of machines and mechanics KB4. how to read machine drawing and machining the part to create the output as defined in the machine drawing KB5. knowledge of metal properties/ metallurgy KB6. basic principles of 5S in manufacturing KB7. aerospace manufacturing standard and procedures such as ISO 9001, AS9100, etc KB8. basic arithmetic and calculation methods for tolerance limits. KB9. operate computing equipment to access and input job tasks information (e.g., drawings, specifications and other online information systems). KB10. knowledge of the coordinate system to identify multiple axes (e.g., X,Y,Z) KB11. Knowledge of correct lifting and rigging procedures such as the selection and inspection of the appropriate slings, cables or chains, to ensure proper handling and distribution of weight when using lifting . Skills:- Core Skills/ Generic Skills:- Writing skills The user/ individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SA1. write basic level notes and observations SA2. draw basic level drawings and charts Reading skills The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SA3. read & comprehend documents and notes, process documentation & control plan SA4. interpret/ comprehend the information given in the documents and notes SA5. read and interpret symbols given on equipment and work area SA6. read machine drawings/ engineering drawings, sketches. Oral Communication (Listening and Speaking skills) The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SA7. discuss task lists and job requirements with co-workers SA8. effectively communicate information to team members SA9. question supervisor in order to understand the nature of the problem SA10. attentively listen with full attention and comprehend the information given by the speaker Professional Skills Problem Solving and Decision making The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SB1. judge when to ask for help from a supervisor SB2. suggest options to operators in case any issue is observed during operations Plan and Organise The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SB3. plan work assigned on a daily basis and provide estimates of time required for each piece of work SB4. prioritise actions to achieve required outcomes Customer centricity: The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SB5. ensure that customer needs are assessed and every effort is made to provide satisfactory service Problem solving: The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SB6. recognise a work place problem or a potential problem and take action SB7. determine problems needing priority action SB8. gather information and provide assistance as required to solve problem SB9. refer problems outside area of responsibility to approach person Analytical thinking The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SB5. analyse the complexity of work to determine if it can be successfully carried out SB6. ability to visualise the final product from the engineering drawing/ machine drawing, sketch provided by the supervisor SB7. analyse the cause of defects related to e.g. cutting tools, machine, fixtures etc. Desire to learn and take initiatives The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SB8. learn from mistakes by analysing and discussing with peers/ seniors SB9. discuss new ideas and participate in new initiatives SB10. follow instructions and work on areas of improvement identified SB11. complete the assigned tasks with minimum supervision SB12. complete the job defined by the supervisor within the timelines and quality norms Critical Thinking Skills The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SB13. concentrate on task at hand and complete it without errors SB14. apply balanced judgments to different situations Perform post machining activities Performance Criteria Perform minor machine maintenance activities To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to PC1. maintain the machine as per proper operational condition/ perform daily maintenance check PC2. perform minor machine maintenance activities such as oiling or cleaning machine and its components as per the schedules given in the maintenance plan PC3. clean the hydraulic tank/ gauge/ tools/ fixtures as per the cleaning schedule and the process mentioned in the work instruction/ SOP manual PC4. add coolant and lubricant in the machine reservoir as per the SOPs PC5. remove chips from different machine areas and dispose of scrap or waste material into the disposal area in accordance with the company policies and environmental regulations PC6. perform minor repairs and adjustments to the machine and notify the supervisor/ maintenance team when major service/ repair is required PC7. return drawings, tools and other measuring equipment to respective department Perform de- burring activity on the machined components PC8. with the help of the correct tool remove extra burrs, sharp edges, rust and chips from the metal surface PC9. use files, hand grinders, wire brushes, or power tools for performing de-burring operations and ensure usage of Personal Protective Equipment (PPEs) such as eye glasses and hand gloves PC10. trim, scrape, or deburr objects or parts using chisels, scrapers, and other hand tools and equipment PC11. perform shot blasting/ vibro processes for completing de-burring operations (if required) Check quality of machined component PC12. measure the specifications of the finished component and verify conformance as per control plan/ work instruction PC13. use devices like micrometers, vernier calipers, gauges, rulers and any other inspection equipment for measuring specifications with valid calibration status PC14. note down the observations of the basic inspection process and identify pieces which comply with the specified standards PC15. separate the defective pieces into two categories – pieces which can be repaired/ modified and pieces which are beyond repair, and maintain records of each category Tool Changing Process PC16. ensure that any blunt tool is timely and safely replaced by a new tool PC17. replace machine part as per work instructions, using hand tools or notify supervisor/ engineering personnel for taking corrective actions PC18. observe the tool change cycle in order to ensure that the selected tool is transferred to the spindle from magazine after the previous tool is transferred to the magazine from the spindle PC19. ensure that the zero offset value is chosen at the time of tool changing process Knowledge and Understanding Organisational Context The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand: KA1. relevant standards and procedures followed in the company KA2. different types of products manufactured by the company Technical Knowledge The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand: KB1. different types of machining processes KB2. different types of tools used in the machining process and de-burring process KB3. basic principles of 5S in manufacturing KB4. aerospace manufacturing standard and procedures such as ISO 9001, AS9100, etc KB4. post machining processes like deburring KB5. impact of presence of burrs, edges, chips on the final product performance KB6. the application of coolant and lubricants KB7. basic arithmetic and calculation methods Skills Core Skills/ Generic Skills Writing skills The user/ individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SA1. write basic level notes and observations SA2. draw basic level drawings and charts Reading skills The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SA3. read documents and notes SA4. interpret/ comprehend the information given in the documents and notes SA5. read and interpret symbols given on equipment and work area Oral Communication (Listening and Speaking skills) The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SA6. disc u ss task lists and job requirements with co-workers SA7. effectively communicate information to team members SA8. question operator/ supervisor in order to understand the nature of the problem SA9. attentively listen with full attention and comprehend the information given by the speaker. Professional Skills Problem Solving and Decision making The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SB1. judge when to ask for help from a supervisor SB2. suggest options to operators in case any issue is observed during operations Plan and Organise The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SB3. plan work assigned on a daily basis and provide estimates of time required for each piece of work SB4. prioritise actions to achieve required outcomes Customer centricity The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SB5. ensure that customer needs are assessed and every effort is made to provide satisfactory service. Problem solving The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SB6. recognise a work place problem or a potential problem and take action SB7. determine problems needing priority action SB8. gather information and provide assistance as required to solve problem SB9. refer problems outside area of responsibility to approach person Analytical thinking The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SB5. analyse the complexity of work to determine if it can be successfully carried out SB6. ability to visualise the final product from the engineering drawing/ machine drawing, sketch provided by the supervisor SB7. analyse the cause of defects related to e.g. cutting tools, machine, fixtures etc. Desire to learn and take initiatives The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SB8. learn from mistakes by analysing and discussing with peers/ seniors SB9. discuss new ideas and participate in new initiatives SB10. follow instructions and work on areas of improvement identified SB11. complete the assigned tasks with minimum supervision SB12. complete the job defined by the supervisor within the timeline. Maintain 5S at the work premises Performance Criteria Comprehending the safety and security procedures PC1. comply with the organisation’s safety and security policies and procedures PC2. comply with the regulatory guidelines on safe conduct of operations and maintenance of conditions to thwart any acts of unlawful interference PC3. report any identified breaches of safety and security policies and procedures to the designated person PC4. report any theft of organisation property according to the organisation policy PC5. coordinate with other resources at the workplace (within and outside the organisation) to achieve a safe and secure environment PC6. identify and mitigate any safety and security hazards like illness, accidents, fires or acts of unlawful interference if it falls within the limits of the individual’s authority PC7. report any hazards outside the individual’s authority to the relevant person in line with organisational procedures and regulatory guidelines PC8. follow the organisation’s emergency procedures for accidents, fires or acts of unlawful interference PC9. identify and recommend opportunities for improving health, safety, and security to the designated person PC10. ensure that all health and safety records are updated and procedures are well defined Knowledge and Understanding Organisational Context KA1. hazard identification and risk management as defined within the organisational policy and procedures KA2. legislative requirements and organisation’s procedures for maintenance of safety and security standards and individual’s role and responsibilities in relation to this KA3. how and when to report hazards KA4. the limits of responsibility for dealing with hazards KA5. the organisation’s emergency procedures for different emergency situations and the importance of following these KA6. the importance of maintaining high standards of safety and security KA7. implications that any non-compliance with safety and security may have on individuals and the organization. Technical Knowledge KB1. different types of breaches of safety and security and how and when to report these KB2. evacuation procedures for workers KB3. how to summon medical assistance and the emergency services, where necessary KB4. how to use the health, safety and accident reporting procedures and the importance of these KB5. regulatory guidelines on dealing with safety and security emergencies Skills Core Skills/ Generic Skills Writing Skills The user/ individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SA1. complete accurate, well written report in English language detailing the situations of emergency with attention to detail Reading Skills The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SA2. read instructions, guidelines/procedures/rules Oral Communication (Listening and Speaking skills) The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SA3. listen to and orally communicate information with all concerned Professional Skills Decision Making The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SB1. make decisions on a suitable course of action or response if permitted by the authority matrix Plan and Organise The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SB2. monitor efficient functioning of all activities SB3. plan and organise work to achieve targets and deadlines Customer Centricity The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SB4. communicate with customers in a courteous manner SB5. maintain effective relationship with the customers Problem Solving The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SB6. identify trends/common causes for errors and suggest possible solutions to the supervisor / management SB7. identify and correct errors Analytical Thinking The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SB8. analyse best possible solutions (cost, time, effort, etc) suited for operations Critical Thinking The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SB9. concentrate on task at hand and complete it without errors SB10. apply balanced judgments to different situations Work effectively in a team Performance Criteria Support the work team PC1. display courteous and helpful behaviour at all times PC2. take opportunities to enhance the level of assistance offered to colleagues PC3. meet all reasonable requests for assistance within acceptable workplace timeframes PC4. complete allocated tasks as assigned PC5. seek assistance when difficulties arise PC6. use questioning t echniques to clarify instructions or responsibilities, PC7. identify and display a non-discriminatory attitude in all contacts with customers and other staff members Maintain personal presentation PC8. observe appropriate dress code and presentation as required by the workplace, job role and level of customer contact PC9. follow personal hygiene procedures according to organisational policy Develop effective work habits PC10. interpret, confirm and act on workplace information, instructions and procedures relevant to the particular task PC11. interpret, confirm and act on legal requirements with regards to anti- discrimination, sexual harassment and bullying PC12. ask questions to seek and clarify workplace information PC13. plan and organise daily work routine within the scope of the job role PC14. prioritise and complete tasks according to required timeframes PC15. identify work and personal priorities and achieve a balance between competing priorities Knowledge and Understanding Organisational Context KA1. policies and procedures relating to the job role KA2. the value system of the organisation KA3. employee rights and obligations Technical Knowledge KB1. ask questions to identify and confirm requirements KB2. follow routine instructions through clear and direct communication KB3. use language and concepts appropriate to cultural differences KB4. use and interpret non-verbal communication KB5. the scope of information or materials required within the parameters of the job role KB6. consequences of poor team participation on job outcomes KB7. work health and safety requirements Skills Core Skills/ Generic Skills Writing Skills, On the job the individual needs to be able to: SA1. complete documentation accurately SA2. write simple reports when required Reading Skills On the job the individual needs to be able to: SA3. read information accurately SA4. read and interpret data sheets Oral Communication (Listening and Speaking skills) The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SA5. listen to and orally communicate information with all concerned Professional Skills Decision Making On the job the individual needs to be able to: SB1. make appropriate decisions regarding the responsibilities of the job role Plan and Organise The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SB2. monitor efficient functioning of all activities SB3. plan and organise work to achieve targets and deadlines Customer Centricity The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SB4. communicate with customers and other stakeholders in a courteous manner SB5. maintain effective work relationship Problem Solving The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SB6. identify trends/common causes for errors and suggest possible solutions to the supervisor / management SB7. identify and correct errors Analytical Thinking The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SB8. analyse best possible solutions (cost, time, effort, etc.) suited for operations Critical Thinking The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SB9. concentrate on task at hand and complete it without errors SB10. apply balanced judgments to different situations Guidelines for Assessment 1. Criteria for assessment for each Qualification Pack will be created by the Sector Skill Council. Each Performance Criteria (PC) will be assigned marks proportional to its importance in NOS. SSC will also lay down proportion of marks for Theory and Skills Practical for each PC. 2. The assessment for the theory part will be based on knowledge bank of questions created by the SSC. 3. Assessment will be conducted for all compulsory NOS, and where applicable, on the selected elective/option NOS/set of NOS. 4. Individual assessment agencies will create unique question papers for theory part for each candidate at each examination/training center (as per assessment criteria below). 5. Individual assessment agencies will create unique evaluations for skill practical for every student at each examination/training center based on this criterion. 6. To pass the Qualification Pack, every trainee should score a minimum of 60% of aggregate marks to successfully clear the assessment. 7. In case of unsuccessful completion, the trainee may seek reassessment on the Qualification Pack. |








