GDA Nursing Class Note 7
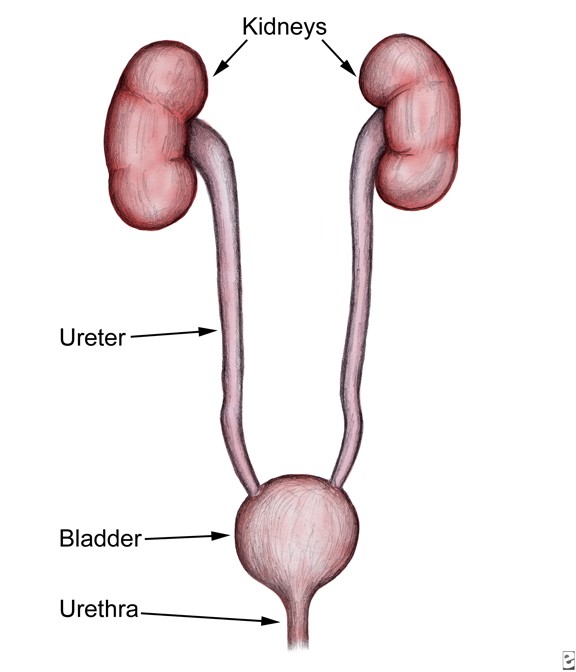
Ureter:
- Definition: The ureters are thin, muscular tubes that serve as the ducts for urine transportation from the kidneys to the urinary bladder.
- Function: The primary function of the ureters is to transport urine produced in the kidneys to the urinary bladder. Peristaltic contractions of the smooth muscle in the ureter walls propel the urine downward.
Urethra:
- Definition: The urethra is a muscular tube that carries urine from the urinary bladder to the outside of the body during urination.
- Function: The main function of the urethra is to expel urine from the bladder during the process of micturition (urination) when the bladder contracts.
Urinary Bladder:
- Definition: The urinary bladder is a hollow, muscular organ that stores urine before it is eliminated from the body through the urethra.
- Capacity: The capacity of the urinary bladder varies between individuals but is typically around 400-600 mL. The stretch receptors in the bladder wall signal the brain when it’s time to urinate, triggering the micturition reflex.
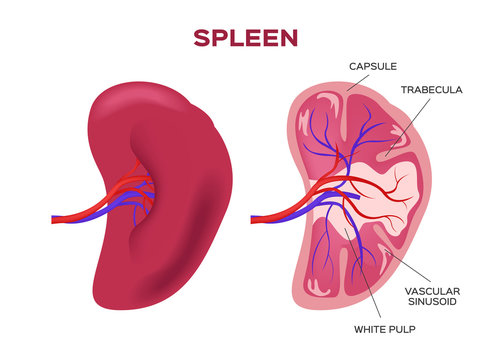
Spleen:
Definition: The spleen is a vital organ located in the upper left quadrant of the abdomen, beneath the ribcage. It is part of the lymphatic system and plays essential roles in immunity, blood filtration, and hematopoiesis (production of blood cells).
Functions of the Spleen:
- Immune Function: The spleen acts as a filter for the blood, removing old or damaged red blood cells, platelets, and pathogens (bacteria, viruses, etc.). It also helps identify and eliminate foreign substances, such as bacteria and dead cells, through phagocytosis.
- Hematopoiesis: During fetal development and in certain pathological conditions, the spleen can act as a site for the production of red blood cells and other blood components. However, the bone marrow is the primary site for hematopoiesis in healthy adults.
- Blood Storage: The spleen acts as a reservoir for red blood cells and platelets, releasing them into the bloodstream when needed, such as during physical exertion or in response to bleeding.
- Iron Metabolism: The spleen is involved in recycling iron from the breakdown of hemoglobin in old red blood cells. This iron is then returned to the bone marrow for the production of new red blood cells
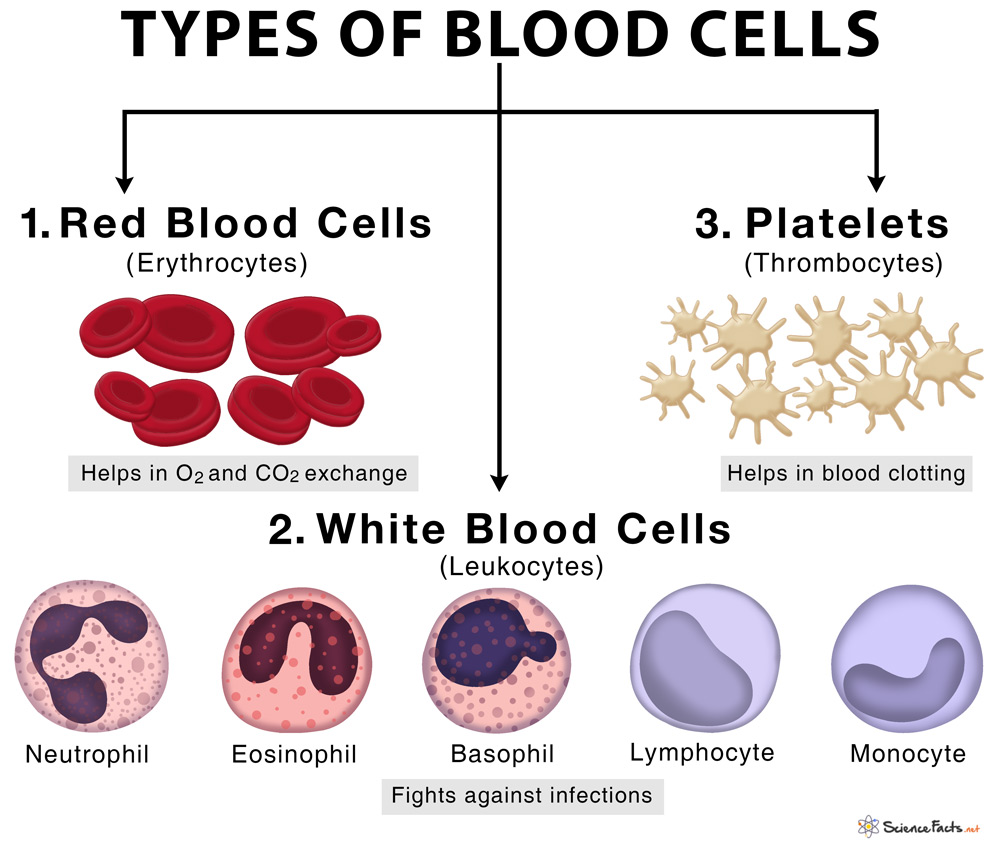
Blood cells:
- Definition: Blood is a specialized fluid connective tissue that circulates throughout the body, delivering essential substances such as oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and immune cells to various tissues and organs. It also plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis and defending the body against infections and foreign invaders.
- Composition:
- Blood is composed of several components: plasma, red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), and platelets (thrombocytes).
- Plasma is the liquid portion of blood, making up about 55% of total blood volume. It consists mainly of water, along with proteins, electrolytes, hormones, waste products, and other substances.
- Red blood cells are responsible for carrying oxygen from the lungs to the body’s tissues. They contain hemoglobin, a protein that binds to oxygen and gives blood its characteristic red color.
- White blood cells are crucial for the immune system. They defend the body against infections and foreign invaders, and they come in different types with specific functions, such as neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils.
- Platelets are essential for blood clotting and wound healing. When a blood vessel is damaged, platelets aggregate at the site to form a plug, preventing excessive bleeding.
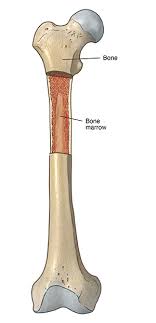
Bone marrow is a soft, spongy tissue found inside the bones of the body. It is a vital component of the hematopoietic system, responsible for the production of blood cells and platelets.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.