GDA Nursing Class Notes 10
Surgical Mask:
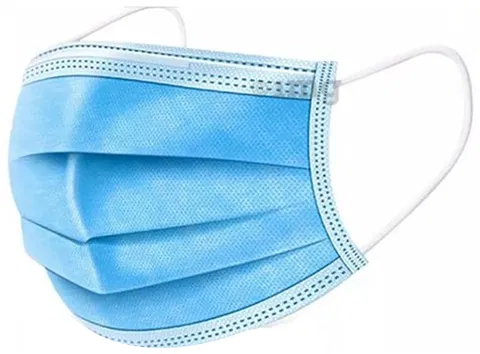
- Purpose: Surgical masks are primarily designed to protect others from the wearer’s respiratory droplets and prevent the spread of infections, particularly during medical procedures, surgeries, and in healthcare settings.
- Filtration: They typically have three layers of material that offer varying degrees of filtration for airborne particles and droplets. The inner layer is absorbent, the middle layer acts as a filter, and the outer layer repels water and fluids.
Hand Gloves:
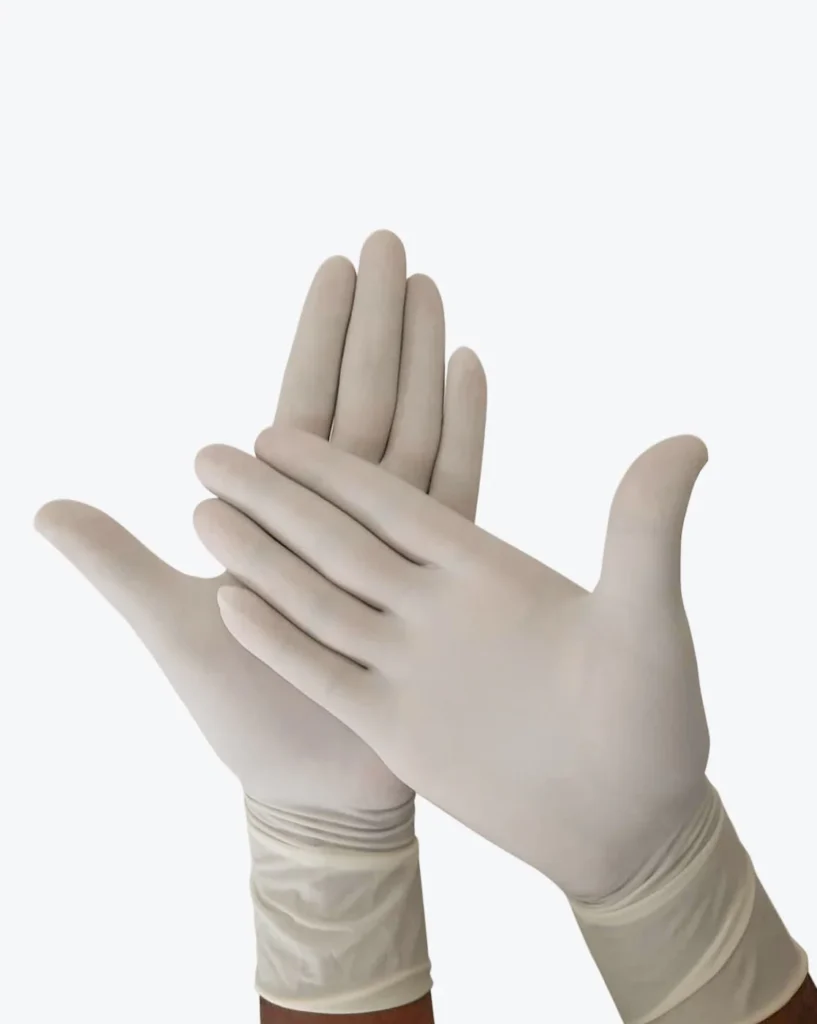

- Purpose: Hand gloves are designed to protect the wearer’s hands from direct contact with harmful substances, chemicals, germs, or other potential hazards.
- Material: Gloves can be made of various materials like latex, nitrile, vinyl, or rubber, each with its unique properties.
sterilization drums:
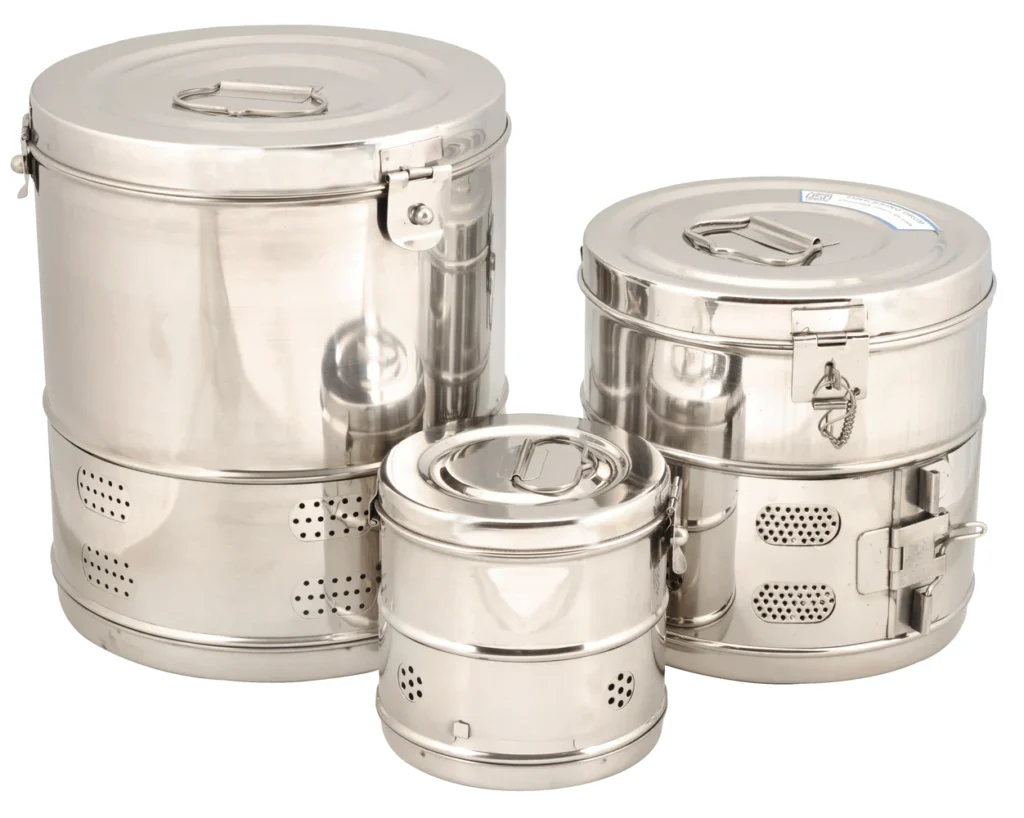

- Purpose: The primary purpose of a sterilization drum is to hold and protect medical instruments, supplies, and equipment during the sterilization process. It ensures that the items inside are exposed to high-temperature steam, which kills or inactivates pathogens, such as bacteria, viruses, and spores.
- Material: Sterilization drums are typically made of sturdy and durable materials such as stainless steel. This ensures they can withstand the high temperatures and pressures of the autoclave sterilization process without getting damaged.
autoclave:
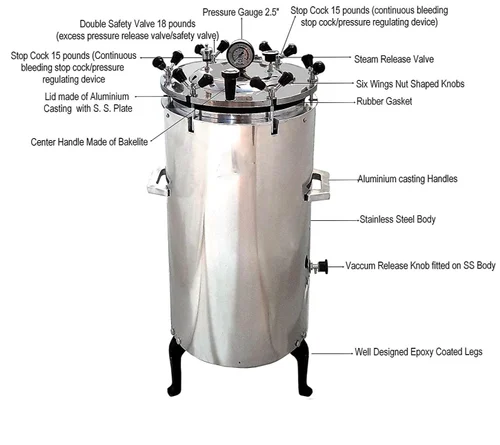
- Purpose: The primary purpose of an autoclave is to sterilize items by subjecting them to high-temperature steam under pressure. The process effectively kills or inactivates microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and spores, making the items safe for use in medical procedures or research.
- Sterilization method: Autoclaves use moist heat as the sterilization method, employing high-pressure saturated steam to achieve the desired effect. The heat and steam penetrate the items, effectively destroying any harmful microorganisms present.
ventilators:
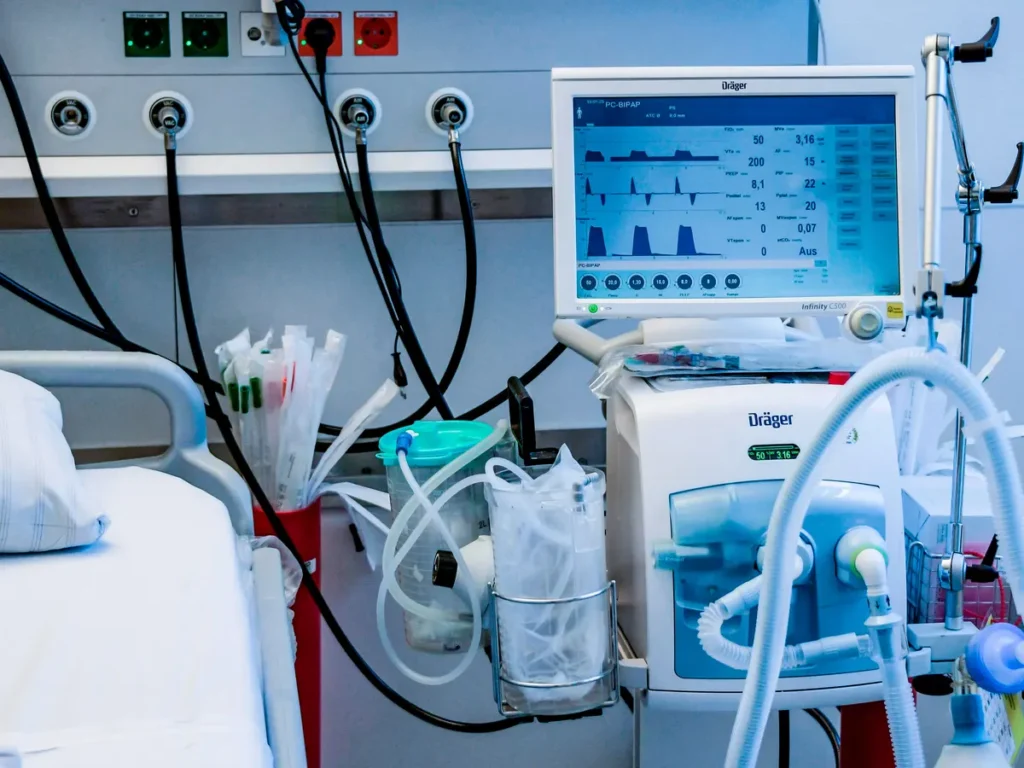
- Purpose: Ventilators are used to provide mechanical ventilation to individuals who are unable to breathe adequately on their own. They deliver oxygen to the lungs and remove carbon dioxide, maintaining appropriate gas exchange and oxygenation in the body.
- Types: There are different types of ventilators, including invasive ventilators (endotracheal intubation or tracheostomy) that require a tube inserted into the airway, and non-invasive ventilators (e.g., BiPAP, CPAP) that deliver air through a mask, typically used for patients with less severe respiratory issues.
- Indications: Ventilators are used in various medical scenarios, such as during anesthesia for surgeries, in intensive care units (ICUs) to support patients with respiratory failure, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), pneumonia, or other critical conditions that affect breathing.
ECG machines:
- Purpose: The primary purpose of an ECG machine is to diagnose and monitor heart conditions by recording the electrical impulses generated by the heart as it contracts and relaxes.
- Electrodes: ECG machines use electrodes that are attached to specific points on the patient’s skin, typically on the chest, arms, and legs. These electrodes detect and transmit the electrical signals from the heart to the ECG machine.
- Leads: The ECG machine records the electrical activity of the heart from different angles using leads. A standard 12-lead ECG is the most common and provides information about the heart’s electrical activity from 12 different views.

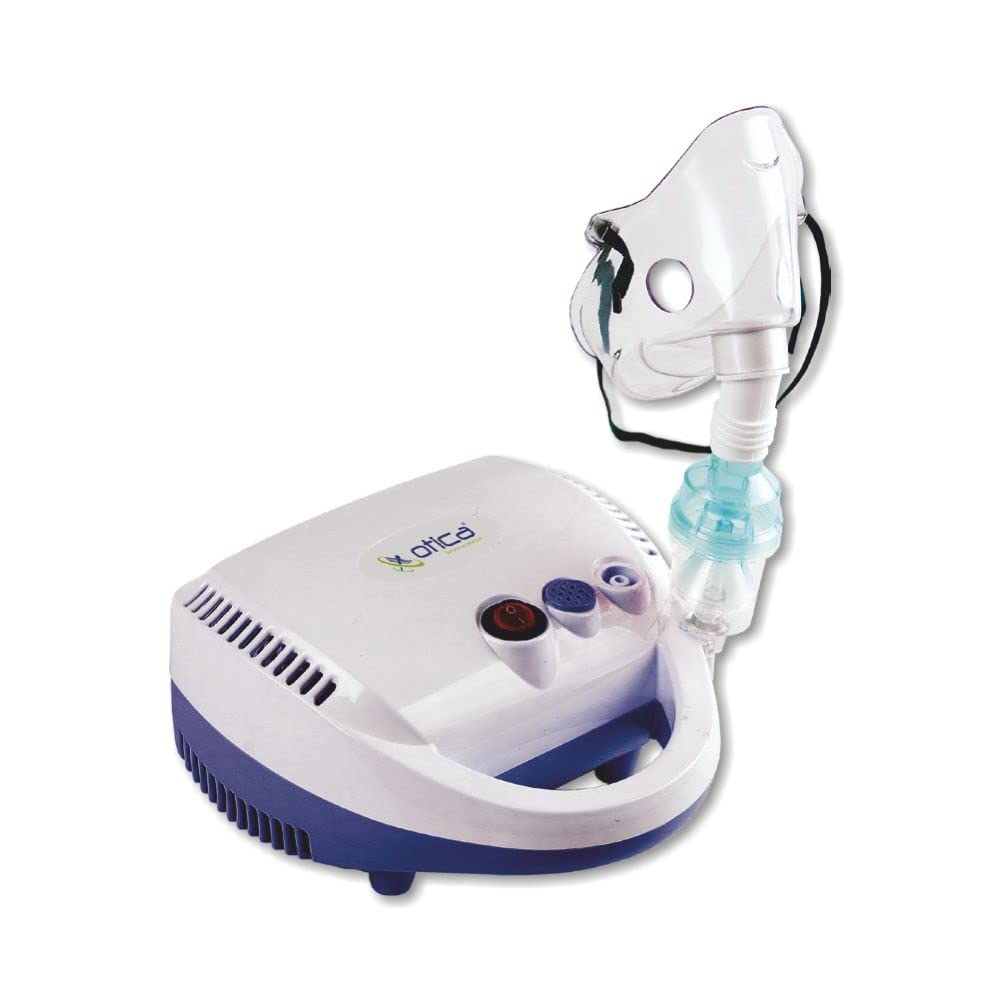
Nebulizers
- Purpose: Nebulizers are primarily used to administer medications for respiratory conditions such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), bronchitis, and other lung-related issues.
- Types: There are two main types of nebulizers – jet nebulizers and ultrasonic nebulizers. Jet nebulizers use compressed air or oxygen to convert liquid medication into a mist, while ultrasonic nebulizers use high-frequency vibrations.
- Medication delivery: Nebulizers can deliver various types of medications, including bronchodilators (e.g., albuterol), corticosteroids (e.g., budesonide), and other respiratory medications.
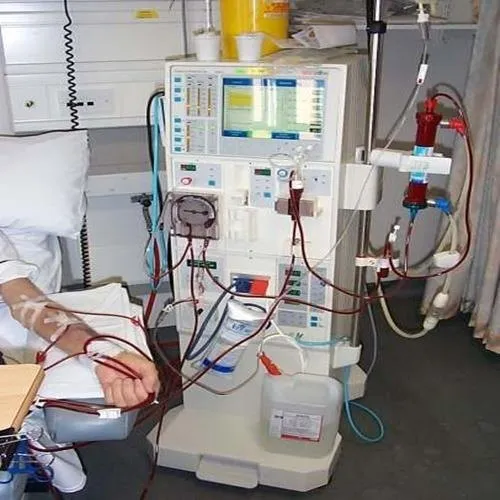
Hemodialysis machines:
- Purpose: Hemodialysis machines are used to perform hemodialysis, a process where the patient’s blood is filtered through a dialyzer (artificial kidney) to remove waste products, toxins, and excess fluids from the bloodstream.
- Dialyzer: The dialyzer is a critical component of the hemodialysis machine. It consists of a semipermeable membrane that allows waste products and excess fluids to pass through while retaining essential substances like red blood cells and proteins.
- Blood Access: Hemodialysis machines require a vascular access site to connect the patient’s bloodstream to the machine. The most common access points are arteriovenous fistulas, arteriovenous grafts, or central venous catheters.
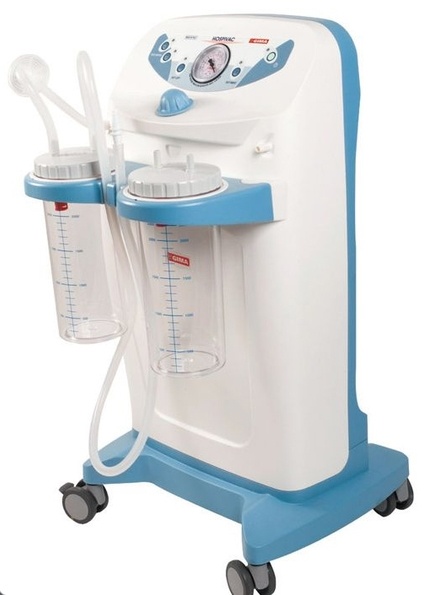
Aspirators:
Aspirators have various applications across different industries and domains. Some common uses include:
- Medical and Healthcare: Aspirators are used to remove fluids, such as mucus or secretions, from the airways during medical procedures or to assist in suctioning during surgery.
- Laboratory: In scientific settings, aspirators are used to aspirate liquids from one container to another, such as in pipetting or sample preparation.
- Industrial: Aspirators can be employed in industrial processes to remove dust, fumes, or other gases from the air in manufacturing or chemical processes.