Rigging Artiste (1 years diploma)
Rigging Artiste click here
Brief Job Description: Individuals at this job are responsible for creating computer
generated controls/rigs for movements in models used for animation under close
supervision
Personal Attributes: This job requires the individual to write computer scripts and
programs to create the desired rigs in models. The individual must know
programming languages such as C, C++ etc. and software such as Autodesk Maya,
3D Studio Max etc. The individual must also have a good understanding of the
human anatomy, skeleton structure, joints, facial muscles etc. The individual
must be well-versed with the principles of 3D modelling and animation.
Qualifications Pack For Rigging Artist
Keywords /Terms
Description
Budget Budget is an estimate of the total cost of production that may include a
break-up of cost components
Compositing Compositing is the process of combining layers of images/elements into a
single frame
Clean-up Refining the interim/rough animation
Creative Brief Creative brief is a document that captures the key questions that serve as
a guide for the production including the vision, objective of the project,
target audience, timelines, budgets, milestones, stakeholders etc.
Key Frame Key Frames are the key poses, usually the start and end poses for a
particular animation sequence
Modelling Modelling is the process of creating three-dimensional models for
animation using a specialised software application.
Rendering Rendering is the process of converting three-dimensional models into twodimensional images with 3D effects
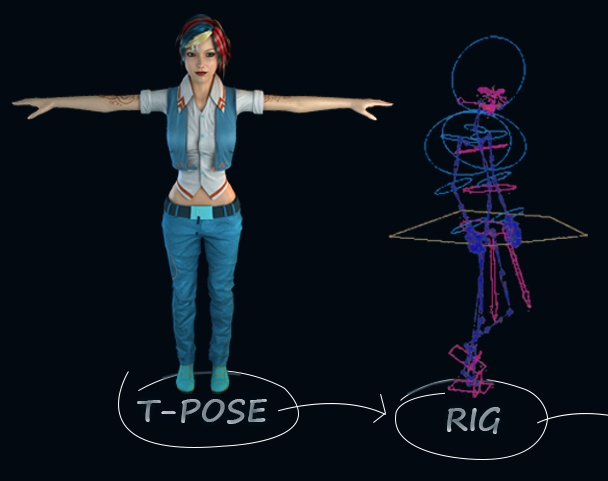
Rigging Rigging is the process of adding joints to a static three-dimensional model
to aid movement during posing
Timelines Timelines is a listing of dates by which the production milestones/stages
need to be completed
Sector Sector is a conglomeration of different business operations having similar
businesses and interests. It may also be defined as a distinct subset of the
economy whose components share similar characteristics and interests.
Sub-sector Sub-sector is derived from a further breakdown based on the
characteristics and interests of its components.
Vertical Vertical may exist within a sub-sector representing different domain areas
or the client industries served by the industry.
Occupation Occupation is a set of job roles, which perform similar/related set of
functions in an industry
Function Function is an activity necessary for achieving the key purpose of the
sector, occupation, or area of work, which can be carried out by a person
or a group of persons. Functions are identified through functional analysis
and form the basis of OS.
Sub-functions Sub-functions are sub-activities essential to fulfill the achieving the
objectives of the function.
Job role Job role defines a unique set of functions that together form a unique
employment opportunity in an organization.
Occupational Standards
(OS)
OS specify the standards of performance an individual must achieve when
carrying out a function in the workplace, together with the knowledge and
understanding they need to meet that standard consistently. Occupational
Standards are applicable both in the Indian and global contexts.
Performance Criteria Performance Criteria are statements that together specify the standard of
performance required when carrying out a task
National Occupational
Standards (NOS)
NOS are Occupational Standards which apply uniquely in the Indian
context.

Qualifications Pack
Code
Qualifications Pack Code is a unique reference code that identifies a
qualifications pack.
Qualifications Pack For Rigging Artist
Keywords /Terms Description
NOS National Occupational Standard(s)
QP Qualifications Pack
NSQF National Skill Qualifications Framework
NVEQF National Vocational Education Qualifications Framework
NVQF National Vocational Qualifications Framework
Qualifications Pack(QP) Qualifications Pack comprises the set of OS, together with the educational,
training and other criteria required to perform a job role. A Qualifications
Pack is assigned a unique qualification pack code.
Unit Code Unit Code is a unique identifier for an Occupational Standard, which is
denoted by an
Unit Title Unit Title gives a clear overall statement about what the incumbent should
be able to do.
Description Description gives a short summary of the unit content. This would be
helpful to anyone searching on a database to verify that this is the
appropriate OS they are looking for.
Scope Scope is the set of statements specifying the range of variables that an
individual may have to deal with in carrying out the function which have a
critical impact on the quality of performance required.
Knowledge and
Understanding
Knowledge and Understanding are statements which together specify the
technical, generic, professional and organizational specific knowledge that
an individual needs in order to perform to the required standard.
Organizational Context Organizational Context includes the way the organization is structured and
how it operates, including the extent of operative knowledge managers
have of their relevant areas of responsibility.
Technical Knowledge Technical Knowledge is the specific knowledge needed to accomplish
specific designated responsibilities.
Core Skills/Generic
Skills
Core Skills or Generic Skills are a group of skills that are key to learning and
working in today’s world. These skills are typically needed in any work
environment. In the context of the OS, these include communication
related skills that are applicable to most job roles.
Description
NOS National Occupational Standard(s)
QP Qualifications Pack
NSQF National Skill Qualifications Framework
NVEQF National Vocational Education Qualifications Framework
NVQF National Vocational Qualifications Framework
Interpret the script/ brief/ storyboard
Description This OS unit is about interpreting the script/ brief/ storyboard for the animation
process
Scope This unit/task covers the following:
Interpretation of script/ brief/ storyboard
Performance Criteria (PC) w.r.t. the Scope PeElement Performance Criteria
Interpretation of
script/ brief/
storyboard
To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to:
PC1. understand the script, brief and storyboard from the art director and character
designers
PC2. understand the design brief in context of his/her job (appearance, complexion,
dressing, moods, personalities, expressions etc.)
PC3. understand the requirements (number, types, duplicates etc.)
PC4. understand the specifications (dimensions, operating parameters etc.)
PC5. understand the technical needs of the project relevant to his/ her job role
(Television, Film, Gaming, Internet, DVD etc.)
PC6. be aware and responsible of his/her role in the pre-production, production and
post-production process
Knowledge and Understanding (K)
A. Organizational
Context
(Knowledge of the
company /
organization and
its processes)
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand:
KA1. the creative vision and elements of production relevant to his/her job role
KA2. the project pipeline/schedule and timelines relevant to their work
KA3. the intended purpose/ end-use of the models that need to be created
B. Technical
Knowledge
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand:
KB1. principles of animation
KB2. human anatomy, skeleton structure, joints, facial muscles etc.
KB3. human mannerisms, emotions, behavior, facial expressions etc.
KB4. techniques and workflow
KB5. drawing and illustration techniques
KB6. how to prepare an output that is consistent with the creative look of the
production and in accordance to the script and design brief
KB7. the sources for research and reference material

KB8. applicable copyright norms and intellectual property rights
KB9. applicable health and safety guidelines
Writing Skills
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to:
SA1. document notes while understanding the brief, requirements and
specifications from the art director and character designers to refer to
during the production process
Reading Skills
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to:
SA2. read and understand the design brief and character pack
SA3. research links, videos, artwork etc. that can be used as references
Oral Communication (Listening and Speaking skills)
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to:
SA4. understand the design brief and requirements from the Art Director and
character designers
B. Professional Skills Plan and Organize
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to:
SB1. breakup the tasks required and estimate the time required for each task, so as
to manage own work in assigned time schedule
Problem Solving
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to:
SB2. identify any creative problems that may arise during the production and work
back with the art director and character designers to find suitable solutions to
address them
SB3. handle technical issues such as pipeline concerns, optimizing efficiency of
assets and asset integration in collaboration with peers and under supervision
of the art director
Decision making
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to:
SB4. make decisions related to the way the script will be represented visually
Analytical Thinking
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to:
SB5. have a keen eye for detail and maintain an aesthetic sense towards the final
output
Critical Thinking
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to:
SB6. appraise the quality of the references gathered (storyboard/character turn
around/pose sheet/facial expressions/etc) to ensure it is in line with the initial
concept and quality standards
Customer Centricity
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to:
SB7. check that the references/interpretations meets customer requirements
Rig models for movements
Description This OS unit is about creating computer generated rigs for movement of models under
close supervision
Scope This unit/task covers the following:
Creating rigs for models (including creating movements of characters {Bends,
Stretches, Expressions}, Accessories, objects, props, sets, locations, bipeds,
quadrupeds, Hair/fur simulation, Cloth simulation)
Performance Criteria (PC) w.r.t. the Scope
Element Performance Criteria
Creating rigs for
models
To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to:
PC1. create user interfaces and controls for movements in the models according to
the design brief (appearance, expressions, movements, dramatic poses etc.),
and specifications (mobility, operating parameters, hierarchy of movement
etc.) under supervision of the animator
PC2. create prototypes/pilots for testing
PC3. ensure that the final rigs are clean, efficient, have realistic movements (using
muscle based rigging) and are animation friendly
Knowledge and Understanding (K)
A. Organizational
Context (Knowledge
of the company /
organization and its
processes)
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand:
KA1. the creative vision and elements of production relevant to his/her job role
KA2. the pipeline/schedule and timelines relevant to their work
KA3. the intended purpose/ end-use of the models that need to be created
B. Technical Knowledge
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand:
KB1. the principles of 3D modelling and animation
KB2. human anatomy, skeleton structure, joints, facial muscles etc.
KB3. rigging principles, processes, systems and techniques like FK, IK etc.
KB4. fundamentals of mathematics and engineering
KB5. how to calculate a rig in the fastest possible manner
KB6. how to write computer scripts and programs to create the desired rigs in
models
KB7. the breaking points for the rig
KB8. how primary movements (movements, facial expressions, gestures etc.) would
affect on secondary animation (of clothing, accessories etc.)
KB9. how to work on software such as Autodesk Maya, 3D Studio Max, Blender etc.
KB10. programming languages such as C, C++, Python, MEL etc.
KB11. how to develop rigs for models consistent with the creative look of the
production and in accordance to the script and design brief
KB12. basics of modeling to maintain a surface flow as per rigging requirements
KB13. the sources for research and reference material
KB14. how to test the rigs using phonemes test, extreme animation test, expression
test, cloth test with motion, jewel motion test etc.
KB15. applicable health and safety guidelines
Writing Skills
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to:
SA1. document notes on the rigging points to be created for different models to
assist during the rigging process
Reading Skills
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to:
SA2. read and understand the script and storyboard to understand the movements
demanded of the script
SA3. gather references and drawings to compare with real-life movements and help
define the rigging points
Oral Communication (Listening and Speaking skills)
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to:
SA4. understand the design brief and rigging points to be created from the art
director, character designers and animators
SA5. collaborate with modelers and animators during the testing phase to ensure
that the model will meet animation requirements
SA6. present the final character models to the Art Director and solicit feedback
B. Professional Skills Plan and Organize
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to:
SB1. plan and prioritise own work according to the requirements and agreed
timelines

SB2. identify reuse of rigs created earlier or available on the internet
Problem Solving
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to:
SB3. identify any creative problems that may arise during the production and work
back with the art director and character designers to find suitable solutions to
address them
Critical Thinking
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to:
SB4. create rigs in accordance to the needs of the animator including
implementation of “Custom” Controls.
Decision making
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to:
SB5. manage creative decisions as per the client inputs while rigging 3D models
Customer Centricity
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to:
SB6. Manage deadlines and revert on corrections or rework as per the
client/animators inputs while rigging 3D models
Analytical Thinking
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to:
SB7. have a keen eye for detail and maintain an aesthetic sense towards colour
Shapes, forms and software capabilities of the final output
Test computer generated rigs
Description This OS unit is about testing computer generated rigs for movement of models
Scope This unit/task covers the following:
Test the rigs for proper functioning
Performance Criteria (PC) w.r.t. the Scope
Element Performance Criteria
Test the rigs for
proper functioning
To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to:
PC1. ensure that the rigs are smooth, intuitive and responsive and meet production
requirements
PC2. ensure rigged assets deform correctly from all required camera positions and
angles
PC3. ensure that final rigs are suitable for exhibition on the applicable medium e.g.
feature, television, game, e-learning etc.
PC4. find solutions for complex rigging problems when required
Knowledge and Understanding (K)
A. Organizational
Context
(Knowledge of the
company /
organization and
its processes)
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand:
KA1. the creative vision and elements of production
KA2. the production pipeline/schedule and timelines relevant to their work
KA3. the intended purpose/ end-use of the models that need to be created
B. Technical Knowledge
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand:
KB1. the principles of 3D modelling and animation
KB2. human anatomy, skeleton structure, joints, facial muscles etc.
KB3. rigging principles, processes, systems and techniques like FK, IK etc.
KB4. fundamentals of mathematics and engineering
KB5. how to calculate a rig in the fastest possible manner
KB6. how to write computer scripts and programs to create the desired rigs in
models
KB7. the breaking points for the rig
KB8. how primary movements (movements, facial expressions, gestures etc.) would
affect secondary animation (of clothing, accessories etc.)
KB9. how to work on software such as Autodesk Maya, 3D Studio Max, Blender etc
KB10. programming languages such as C, C++, Python, MEL etc.
KB11. how to develop rigs for models consistent with the creative look of the
production and in accordance to the script and design brief
KB12. basics of modeling to maintain a surface flow as per rigging requirements
KB13. the sources for research and reference material
KB14. how to test the rigs using phonemes test, extreme animation test, expression
test, cloth test with motion, jewel motion test etc.
KB15. applicable health and safety guidelines
Writing Skills
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to:
SA1. document notes on the rigging points to be created for different models to
assist during the rigging process
Reading Skills
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to:
SA2. read and understand the script and storyboard to understand the movements
demanded of the script
SA3. gather references and drawings to compare with real-life movements and help
define the rigging points
Oral Communication (Listening and Speaking skills)
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to:
SA4. understand the design brief and rigging points to be created from the Art
Director, character designers and animators
SA5. collaborate with modelers and animators during the testing phase to ensure
that the model will meet animation requirements
SA6. present the final character models to the Art Director and solicit feedback
B. Professional Skills Plan and Organize
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to:
SB1. plan and prioritise own work according to the requirements and agreed
timelines

SB2. identify reuse of rigs created earlier or available on the internet
Problem Solving
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to:
SB3. identify any creative problems that may arise during the production and work
back with the art director and character designers to find suitable solutions to
address them
Critical Thinking
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to:
SB4. create rigs in accordance to the needs of the animator including
implementation of “Custom” Controls.
Decision making
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to:
SB5. manage creative decisions as per the client inputs while testing rigs for
animation for desired poses.
Customer Centricity
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to:
SB6. prioritize work according to the requirements of facial/lipsync /animation
departments
Analytical Thinking
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to:
SB7. have a keen eye for detail and maintain an aesthetic sense towards Shapes .








