How to Take Body Measurement
Taking accurate body measurements is crucial in various fields such as fashion design, fitness training, and healthcare. Proper measurements ensure that clothing fits well, fitness progress is accurately tracked, and health assessments are precise. This guide will cover essential techniques and tips for measuring different parts of the body effectively.
Tools Needed
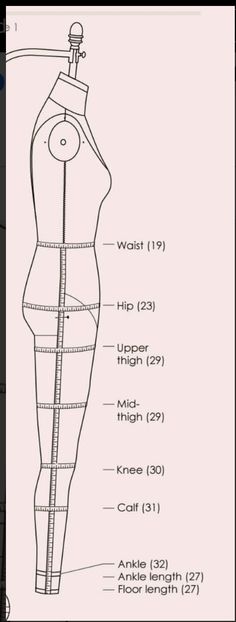
Before starting, gather the following tools:
- Measuring Tape: A flexible tape measure is essential for most body measurements.
- Body Fat Calipers: For measuring skinfold thickness in body fat assessments (optional but recommended for fitness professionals).
- Pen and Paper: To record measurements.
- Assistant: Sometimes, having someone assist ensures more accurate measurements, especially for hard-to-reach areas.
General Guidelines
- Consistency: Always use the same techniques and tools to ensure consistency in measurements.
- Posture: Stand or sit comfortably in a relaxed posture. For accurate results, avoid tensing muscles.
- Clothing: Ideally, measurements should be taken on bare skin or over form-fitting clothing to reduce inaccuracies caused by bulky garments.
Step-by-Step Measurement Guide
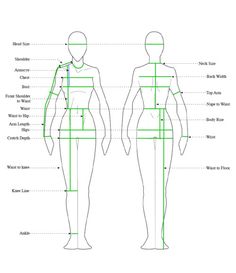
1. Height
- Method: Stand barefoot against a wall, heels together, and back straight.
- Measurement: Use a measuring tape to measure from the floor to the top of the head.
2. Neck
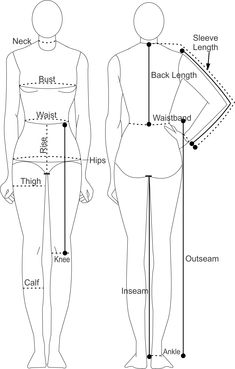
- Method: Stand or sit comfortably with the head in a neutral position.
- Measurement: Place the tape around the neck, just below the Adam’s apple (for men) or at the base of the neck (for women). Allow enough room for a finger to fit between the tape and the neck for comfort.
3. Chest/Bust
- Method: Relax the arms by the sides (for men) or hold them straight out to the sides (for women).
- Measurement: Wrap the tape measure around the chest at the fullest part of the chest or bust. Ensure the tape is parallel to the floor and snug but not tight.
4. Waist
- Method: Stand relaxed with feet together.
- Measurement: Find the natural waistline (usually the smallest part of the torso above the belly button). Wrap the tape measure around the waist, keeping it snug but not squeezing the skin.
5. Hips
- Method: Stand with feet together.
- Measurement: Measure around the fullest part of the hips, usually around the hip bones. Keep the tape measure parallel to the floor.
6. Inseam
- Method: Stand upright with feet shoulder-width apart.
- Measurement: Measure from the crotch to the bottom of the ankle or desired pant length.
7. Arm Length
- Method: Extend one arm out to the side.
- Measurement: Measure from the shoulder bone (where the arm meets the shoulder) to the wrist bone. Keep the arm slightly bent.
8. Thigh and Calf
- Method: Stand with legs slightly apart.
- Measurement: Measure around the thickest part of the thigh and calf muscles, ensuring the tape is snug but not tight.
9. Body Fat (Using Calipers)
- Method: Pinch the skinfold at various sites (e.g., triceps, abdomen) with the calipers.
- Measurement: Read the caliper measurement and record. Repeat for accuracy and calculate the average if needed.
Recording and Analyzing Measurements
- Record: Write down all measurements clearly and label them accordingly.
- Analyze: Compare measurements over time to track progress (e.g., fitness measurements) or use them for garment sizing.
Conclusion
Accurate body measurements are essential for many practical purposes, from designing clothes that fit perfectly to monitoring health and fitness progress. By following these guidelines and techniques, you can ensure that your measurements are precise and reliable, benefiting both yourself and those you work with in various professional capacities.
Taking the time to learn and practice these measurement techniques will enhance your skills and ensure that you can consistently obtain accurate measurements for any purpose.
This comprehensive guide covers the essential aspects of taking body measurements, providing a solid foundation for anyone learning this skill. Adjustments can be made based on specific requirements or additional tools available, ensuring flexibility in application across different fields.
