GDA Nursing Class Notes 02
PULSE
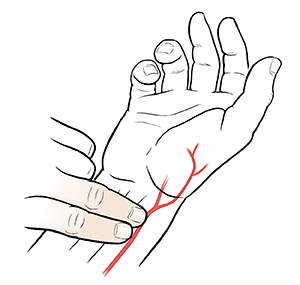
•Pulse is number of the heart beats acquiring per minute.
•Pulse is the wave occurring in an artery in response to the pumping action of heart which is felt and measured by placing the fingers on the artery.
The pulse is defined as the rhythmic expansion and contraction of the arteries, which is typically caused by the beating of the heart as it pumps blood throughout the body. It is most commonly measured at various pulse points in the body, such as the wrist (radial artery), neck (carotid artery), or groin (femoral artery). The pulse rate is usually expressed as the number of beats per minute (BPM) and is a vital sign used to assess a person’s heart rate and overall cardiovascular health. It can provide important information about the strength, regularity, and overall condition of the heartbeat.
•Normal pulse rate is 70-80(average 72 ) beats/min.
COMMON SITES

1.Temporal
2.Carotid
3.Apical
4.Brachial
5.Radial
6.Ulnar
7.Femoral
8.Popliteal
9.Posterior tibial
10.Dorsalis pedis
COMMON PROBLEMS.
•Tachycardia:-
The pulse rate more than 100 beats/min.
• Bradycardia:-
The pulse rate is less than 60 beats/min.
SATURATION OF OXYGEN
Oxygen saturation is typically measured noninvasively using a device called a pulse oximeter, which is usually attached to a person’s fingertip, earlobe, or other areas with good blood flow. The measurement is expressed as a percentage, with 100% representing all available hemoglobin binding sites being occupied by oxygen. A normal and healthy oxygen saturation level is generally considered to be in the range of 95% to 100%, although values slightly below this range may still be acceptable in certain circumstances.
•SpO2 is measured by the help of a pulse oximeter.