Free Medical Laboratory Technician Course (1year Diploma Course)
Medical Laboratory Technician (MLT):– also referred to as Clinical Laboratory Science professionals, Medical Technologists and Medical Laboratory Scientists
Brief Job Description: -The Medical laboratory technician perform complex tests for diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of disease. These professionals are responsible for supporting and assisting doctors/ scientists in their day-to-day working in a variety of roles. They function as the main support to biomedical scientists in pathology laboratories Medical Laboratory Technician Course.
Personal Attributes: -This job requires the MLT to work in association with doctors, pathologists and scientists. Essential attributes include empathy, orientation to detail, dexterity, critical thinking, persistence and ability to work in stressful environment.
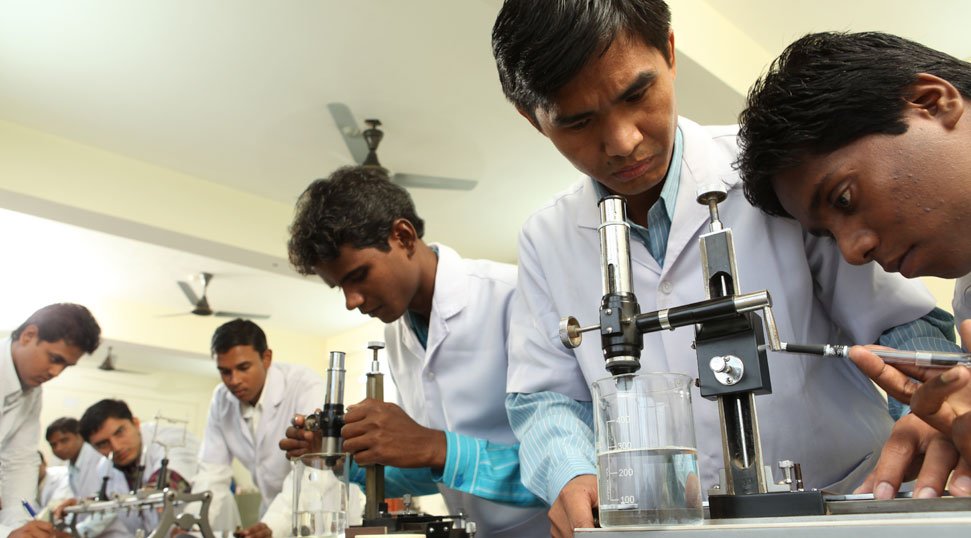


Correctly collect, transport, receive, accept or reject, store blood/urine/stool and tissue samples Medical Laboratory Technician Course :-To be competent, the user/individual on the job must:
PC1. Identify information by categorising, estimating, recognising the differences or similarities, and detecting changes in circumstances or events
PC2. Have a fair knowledge of blood cell biology
PC3. Perform phlebotomy effectively
PC4. Respond to emergencies as they arise
PC5. Apply the principles of genetics and immunology to transfusion practice
PC6. Generate or use different sets of rules for combining or grouping things in different ways
PC7. Be up-to-date technically and apply new knowledge to the job
PC8. Know how to follow sample acceptance and rejection criteria
PC9. Know how to pack, transport and store the samples Medical Laboratory Technician Course.
Conduct analysis of body fluids/ samples:-To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to:

PC1. Identify information by categorising, estimating, recognising differences or similarities, and detecting changes in components of body fluids/ samples
PC2. Understand how samples of body fluids/ samples are collected and analysed
PC3. Know what is implied by the presence of abnormal constituents in body fluids/ samples
Maintain, operate and clean laboratory equipment Medical Laboratory Technician Course:- To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to:
PC1. Inspect equipment, structures, or materials to identify the cause of errors or other problems or defects
PC2. Concentrate on a task over a period of time without being distracted Medical Laboratory Technician Course.
PC3. Have sound knowledge of the functioning of lab equipment’s and protocols for their cleaning and calibration
Provide technical information about test results- PC1. Process information by compiling, coding, categorising, calculating, tabulating, auditing or verification of data
PC2. Generate or use different sets of rules for combining or grouping things in different way
PC3. Concentrate on a task over a period of time without being distracted


Prepare and document medical tests and clinical results Medical Laboratory Technician Course:- To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to:
PC1. Identify information by categorising, estimating, recognising differences or similarities, and detecting changes in circumstances or events
PC2. Inspect equipment, structures, or materials to identify the cause of errors or other problems or defects
PC3. Process information by compiling, coding, categorising, calculating, tabulating, auditing or verification of data
PC4. Apply general rules to specific problems to produce answers that make sense Medical Laboratory Technician Course.
PC5. Combine pieces of information to form general rules or conclusions (includes finding a relationship among seemingly unrelated events)
Establish and monitor quality assurance programs:- PC1. Swab the skin with an antiseptic solution
PC2. Prepare the needle of very fine diameter for the process
PC3. Take and record the vitals (pulse, blood pressure, temperature, etc.) before the procedure is started
PC4. Prepare the equipment and slides for examining the sample
PC5. Maintain adequate supplies of medical and diagnostic supplies
PC6. Arrive at actual demand as accurately as possible Medical Laboratory Technician Course.
PC7. Anticipate future demand based on internal, external and other contributing factors as accurately as possible
PC8. Handle situations of stock-outs or unavailability of stocks without compromising health needs of patients/ individuals

Conducts research under guidance Medical Laboratory Technician Course:- To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to:

PC1. Identify information by categorising, estimating, recognising differences or similarities, and detecting changes in circumstances or events
PC2. Inspect equipment, structures, or materials to identify the cause of errors or other problems or defects
PC3. Apply general rules to specific problems to produce answers that make sense
PC4. Combine pieces of information to form general rules or conclusions (includes finding a relationship among seemingly unrelated events)
PC5. Concentrate on a task over a period of time without being distracted
PC6. Understand the need and importance of research and the protocols for conducting the same

Assist in fine needle aspiration cytology:- To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to:
PC1. Swab the skin with an antiseptic solution
PC2. Prepare the needle of very fine diameter for the process
PC3. Take and record the vitals (pulse, blood pressure, temperature, etc.) before the procedure is started
PC4. Prepare the equipment and slides for examining the sample Medical Laboratory Technician Course.
Ensure availability of medical and diagnostic supplies Medical Laboratory Technician Course:- To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to:
PC1. Maintain adequate supplies of medical and diagnostic supplies
PC2. Arrive at actual demand as accurately as possible
PC3. Anticipate future demand based on internal, external and other contributing factors as accurately as possible
PC4. Handle situations of stock-outs or unavailability of stocks without compromising health needs of patients/ individuals
Act within the limits of one’s competence and authority:- To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to:
PC1. Adhere to legislation, protocols and guidelines relevant to one’s role and field of practice
PC2. Work within organisational systems and requirements as appropriate to one’s role
PC3. Recognise the boundary of one’s role and responsibility and seek supervision when situations are beyond one’s competence and authority
PC4. Maintain competence within one’s role and field of practice
PC5. Use relevant research based protocols and guidelines as evidence to inform one’s practice
PC6. Promote and demonstrate good practice as an individual and as a team member at all times
PC7. Identify and manage potential and actual risks to the quality and safety of practice
PC8. Evaluate and reflect on the quality of one’s work and make continuing improvements Medical Laboratory Technician Course.
Manage work to meet requirements:- To be competent, the user/ individual on the job must be able to:
PC1. Clearly establish, agree, and record the work requirements
PC2. Utilise time effectively
PC3. Ensure his/her work meets the agreed requirements
PC4. Treat confidential information correctly
PC5. Work in line with the organisation’s procedures and policies and within the limits of his/her job role

Practice Code of conduct while performing duties;-
To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to:
PC1. Adhere to protocols and guidelines relevant to the role and field of practice
PC2. Work within organisational systems and requirements as appropriate to the role Medical Laboratory Technician Course.
PC3. Recognise the boundary of the role and responsibility and seek supervision when situations are beyond the competence and authority
PC4. Maintain competence within the role and field of practice
PC5. Use protocols and guidelines relevant to the field of practice
PC6. Promote and demonstrate good practice as an individual and as a team member at all times
PC7. Identify and manage potential and actual risks to the quality and patient safety
PC8. Maintain personal hygiene and contribute actively to the healthcare ecosystem
Follow biomedical waste disposal protocols:- To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to:
PC1. Follow the appropriate procedures, policies and protocols for the method of collection and containment level according to the waste type
PC2. Apply appropriate health and safety measures and standard precautions for infection prevention and control and personal protective equipment relevant to the type and category of waste Medical Laboratory Technician Course.
PC3. Segregate the waste material from work areas in line with current legislation and organisational requirements
PC4. Segregation should happen at source with proper containment, by using different color coded bins for different categories of waste
PC5. Check the accuracy of the labelling that identifies the type and content of waste
PC6. Confirm suitability of containers for any required course of action appropriate to the type of waste disposal
PC7. Check the waste has undergone the required processes to make it safe for transport and disposal PC8. Transport the waste to the disposal site, taking into consideration its associated risks
PC9. Report and deal with spillages and contamination in accordance with current legislation and procedures
PC10. Maintain full, accurate and legible records of information and store in correct location in line with current legislation, guidelines, local policies and protocols Medical Laboratory Technician Course.
Follow infection control policies and procedures:- To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to:
PC1. Preform the standard precautions to prevent the spread of infection in accordance with organisation requirements
PC2. Preform the additional precautions when standard precautions alone may not be sufficient to prevent transmission of infection
PC3. Minimise contamination of materials, equipment and instruments by aerosols and splatter
PC4. Identify infection risks and implement an appropriate response within own role and responsibility PC5. Document and report activities and tasks that put patients and/or other workers at risk
PC6. Respond appropriately to situations that pose an infection risk in accordance with the policies and procedures of the organization
PC7. Follow procedures for risk control and risk containment for specific risks
PC8. Follow protocols for care following exposure to blood or other body fluids as required
PC9. Place appropriate signs when and where appropriate
PC10. Remove spills in accordance with the policies and procedures of the organization
PC11. Maintain hand hygiene by washing hands before and after patient contact and/or after any activity likely to cause contamination
PC12. Follow hand washing procedures
PC13. Implement hand care procedures
PC14. Cover cuts and abrasions with water-proof dressings and change as necessary
PC15. Wear personal protective clothing and equipment that complies with Indian Change protective clothing and gowns/aprons daily, more frequently if soiled and where appropriate, after each patient contact
PC17. Demarcate and maintain clean and contaminated zones in all aspects of health care work
PC18. Confine records, materials and medicaments to a well-designated clean zone
PC19. Confine contaminated instruments and equipment to a well-designated contaminated zone
PC20. Wear appropriate personal protective clothing and equipment in accordance with occupational health and safety policies and procedures when handling waste
PC21. Separate waste at the point where it has been generated and dispose of into waste containers that are colour coded and identified
PC22. Store clinical or related waste in an area that is accessible only to authorised persons
PC23. Handle, package, label, store, transport and dispose of waste appropriately to minimise potential for contact with the waste and to reduce the risk to the environment from accidental release
PC24. Dispose of waste safely in accordance with policies and procedures of the organisation and legislative requirements
PC25. Wear personal protective clothing and equipment during cleaning procedures
PC26. Remove all dust, dirt and physical debris from work surfaces
PC27. Clean all work surfaces with a neutral detergent and warm water solution before and after each session or when visibly soiled
PC28. Decontaminate equipment requiring special processing in accordance with quality management systems to ensure full compliance with cleaning, disinfection and sterilisation protocols
PC29. Dry all work surfaces before and after use PC30. Replace surface covers where applicable
PC31. Maintain and store cleaning equipment
Core Skills /Generic Skills:- The user/ individual on the job needs to know and understand how to:

SA1. Document reports, task lists, and schedules
SA2. Prepare status and progress reports
SA3. Record daily activities
SA4. Update other co-workers
Reading Skills:- The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to:
SA5. Read about changes in legislations and organisational policies
SA6. Keep updated with the latest knowledge
Oral Communication (Listening and Speaking skills):-
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to:
SA7. Discuss task lists, schedules, and work-loads with co-workers
SA8. Give clear instructions to patients and co-workers
SA9. Keep patient informed about progress
SA10.Avoid using jargon, slang or acronyms when communicating with a patient
Professional Skills:-
he user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to:
SB1. Make decisions pertaining to the concerned area of work in relation to job role
Decision Making:- The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to:
SB1. Decide on the level of anticipated demand
SB2. Decide when to procure additional supplies
SB3. Decide quantities of medical supplies to request
Plan and Organise:- The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand:
SB4. How to plan availability of medical supplies
SB5. How to place requestfor supplies ahead of time in order to have adequate supplies at all times
Customer Centricity:- The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to:
SB6. Cater to the need of patients/ individuals for specific medical supplies
Problem Solving:- The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to:
SB7. Handle non-availability of medical supplies or diagnostic kits when required such as ordering from alternate vendors , out right purchase etc.

Technical Knowledge:- The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand:
KB1. The boundaries of one’s role and responsibilities and other team members
KB2. The reasons for working within the limits of one’s competence and authority
KB3. The importance of personally promoting and demonstrating good practice
KB4. The legislation, protocols and guidelines effecting one’s work
KB5. The organisational systems and requirements relevant to one’s role
KB6. The sources of information that can be accessed to maintain an awareness of research and developments in one’s area of work
KB7. The difference between direct and indirect supervision and autonomous practice, and which combination is most applicable in different circumstances

KB8. The risks to quality and safety arising from:
1.Working outside the boundaries of competence and authority
2. Not keeping up to date with best practice
3. Poor communication
4.Insufficient support
5. Lack of resources
KB9. The importance of individual or team compliance with legislation, protocols, and guidelines and organisational systems and requirements
KB10.How to Report and minimise risks
KB11.The principle of meeting the organisation’s needs, and how this should enable one to recognise one’s own limitations and when one should seek support from others
KB12.The processes by which improvements to protocols/guidelines and organisational systems/requirements should be reported
KB13.The procedure for accessing training, learning and development needs for oneself and/or others within one’s organisation
KB14.The actions that can be taken to ensure a current, clear and accurate understanding of roles and responsibilities is maintained, and how this affects the way one work as an individual or part of a team