Free Forensic Specialists Course (6Months)
Forensic Specialist: click here
Forensic Specialist: in some organisations Forensic Specialist is known as Forensic Consultant.
Brief Job Description: The main duties consist of identifying, preserving and seizing digital/electronic forensic evidences, extracting information and data from the digital information or data sources or devices, examining and analyzing the information or data and further reporting and presenting the findings before competent authority.
Personal Attributes: This job may require the individual to work independently
and take decisions for his/her own area of work. The individual should have a high level of analytical thinking ability, passion for information security and attention for detail. The individual should also be ethical, compliance and result oriented, should also be able to demonstrate interpersonal skills, along with willingness to undertake desk-based job with long working hours.
Free Forensics Specialists Course (6Months)
/487041745-56a1e26e3df78cf7726f9adf.jpg)
Identify, preserve and seize digital/electronics devices or records for
investigation of possible breach or crime:
Performance Criteria
To be competent, you must be able to:
PC1. ensure that necessary authorisations and resources are in place to conduct a forensics evidence seizure for an investigation
PC2. ensure that the scene is physically secured to prevent unauthorized access and alteration or damage of the evidence as per containment policies and situational considerations
PC3. survey a physical area and identify potential sources of data that could be evidence
PC4. identify other sources of data and the owner of the same that can be accessed
PC5. identify and obtain materials related to digital communications which are relevant to the investigation
PC6. Ensure identified device or component is up and running however is being disconnected from any network
PC7. check for and terminate any destructive software running on any device while seeking to save as much information as possible
PC8. estimate the relative likely value of each potential data source for the investigation
PC9. identify whether data in the device or record is volatile or non-volatile so that both types of data can be adequately preserved
PC10. create a plan that prioritizes the sources, establishing the order in which the computing devices or records can be acquired
PC11. use forensic tools to collect volatile data
PC12. duplicate non-volatile data sources to collect their data, securing the original non-volatile data sources
PC13. verify and preserve the integrity of the data source device or record in accordance with investigation procedures
PC14. record current state, condition and configuration of digital devices and media and potentially relevant information at the time of seizure
PC15. handle digital devices and media consistent with preserving other potential evidence sources including fingerprints or DNA
PC16. document any activity on the computer, components, or devices by taking photographs or recording any information that may be relevant
PC17. maintain a detailed log of every step that was taken to collect the data, including information about each tool used in the process and handlers
PC18. photograph and label the components of the device making specific reference to ancillary leads and connections to the device
PC19. appropriately package, seal and label the device in accordance with current diligence procedures
PC20. check packaging of forensic items in line with forensic procedures, and identify, record and address any packaging problems
PC21. carefully document each stage of the seizure and investigation
PC22. ensure chain of custody is followed for all digital media acquired in accordance with the rules of evidence
PC23. identify any risks to safety linked to working with forensic items in line with health and safety procedures
PC24. take the necessary actions to minimise any risks linked to working with forensic items
PC25. transport and store forensic items to relevant authorities in line with investigative procedures, and in a way that avoids risk to potential evidence, including loss, breakage, contamination, cross-contamination, degradation, etc.
PC26. record details of the storage, handling, transfer and packaging of forensic items in line with organisational procedures
Organizational
Context
You need to know and understand:
KA1. relevant legislation, policies, procedures, codes of practice, guidelines and applicable standards for seizing and recording electronic evidence sources
KA2. organization’s knowledge base and how to access and update this
KA3. limits of your role and responsibilities and who to seek guidance from
KA4. the organizational systems, procedures and tasks/checklists within the domain and how to use these
KA5. the operating procedures that are applicable to the system(s) being used
KA6. typical response times and service times related to own work area

Technical
Knowledge
You need to know and understand:
KB1. types of electronic evidence, devices containing electronic evidence and external connections to such devices
Table of Content
.KB2. possible electronic evidence sources
KB3. processes for seizing and preserving digital evidence and maintaining chain of custody
KB4. methods of protecting and concealing electronic information including locking, encryption, sealing, etc.
KB5. how to identify and deal with protected and/or concealed systems
KB6. the types of operating systems and how to deal with them
KB7. which system files contain relevant information and where to find those
system files
KB8. how to preserve the information on battery powered devices
KB9. the types of actions necessary to preserve third party and volatile data sources
KB10. do’s and don’ts for seizing and recording electronic evidence sources
KB11. how to keep a record of the seizure process, the condition and state of the device and the reasons why this is important
KB12. knowledge of all aspects of the computer including but not limited to hard drives, networking, and encryption
KB13. the impact of actions on victims and witnesses
KB14. the importance of considering all potentially relevant information in the immediate vicinity
KB15. the actions necessary to safeguard the device for forensic examinations
KB16. how to conduct a preview of the contents of electronic devices
KB17. the need to consider physical forensic examinations and the implications
KB18. the importance of maintaining an accurate contemporaneous record using appropriate methods
KB19. processes for collecting, packaging, transporting, and storing electronic evidence to avoid alteration, loss, physical damage, or destruction of data
KB20. handling memory forensics and volatile evidences
KB21. importance of crime scene management and what does it entail
KB22. internet ports, protocols and services and their usefulness
KB23. Common cyber security solutions
KB24. work on various operating systems
Writing Skills
You need to know and understand how to:
SA1. document call logs, reports, task lists, and schedules with co-workers
SA2. prepare status and progress reports
SA3. write memos and e-mail to customers, co-workers, and vendors to provide them with work updates and to request appropriate information without English language errors regarding grammar or sentence construct and following professional etiquettes
Reading Skills
You need to know and understand how to:
SA4. read about new products and services with reference to the organization and also from external forums such as websites and blogs
SA5. keep abreast with the latest knowledge by reading brochures, pamphlets, and
product information sheets
SA6. read comments, suggestions, and responses to Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) posted on the helpdesk portal
SA7. read policy manual, standard operating procedures and service level agreements relevant to work area
SA8. read emails received from own team, across team and external vendors and clients
Oral Communication (Listening and Speaking skills)
You need to know and understand how to:
SA9. discuss task lists, schedules, and work-loads with co-workers
SA10. give clear instructions to specialists/vendors/users/clients as required
SA11. keep stakeholders informed about progress
SA12. avoid using jargon, slang or acronyms when communicating with a customer, unless it is required
SA13. receive and make phone calls, including call forward, call hold, and call mute
. Professional Skills

Decision Making
You need to know and understand how to:
SB1. follow rule-based decision-making processes
SB2. make decisions on suitable courses of action
Plan and Organize
You need to know and understand how to:
SB3. plan and organize your work to achieve targets and deadlines
Free Forensics Specialists Course (6Months)
Customer Centricity
You need to know and understand how to:
SB3. carry out rule-based transactions in line with customer-specific guidelines,
SB4. procedures, rules and service level agreements
SB5. check your own and/or your peers work meets customer requirements
Problem Solving
You need to know and understand how to:
SB6. apply problem-solving approaches in different situations
SB7. seek clarification on problems from others
Analytical Thinking
You need to know and understand how to:
SB8. analyze data and activities
SB9. configure data and disseminate relevant information to others
SB10. pass on relevant information to others
Critical Thinking
You need to know and understand how to:
SB11. provide opinions on work in a detailed and constructive way
SB12. apply balanced judgments to different situations
Technical Skills
You need to know and understand how to:
SC1. analyze the system architecture and design
SC2. evaluate operating system and file system configurations
SC3. configure networking and security devices
SC4. manage backups and storages
SC5. deploy and configure application systems
SC6. use word processors, spreadsheets and presentations
SC7. stay abreast of the latest developments as per industry standards and security tools to ensure that corporate security methods and tools

Extract relevant data or information from digital forensic evidences;
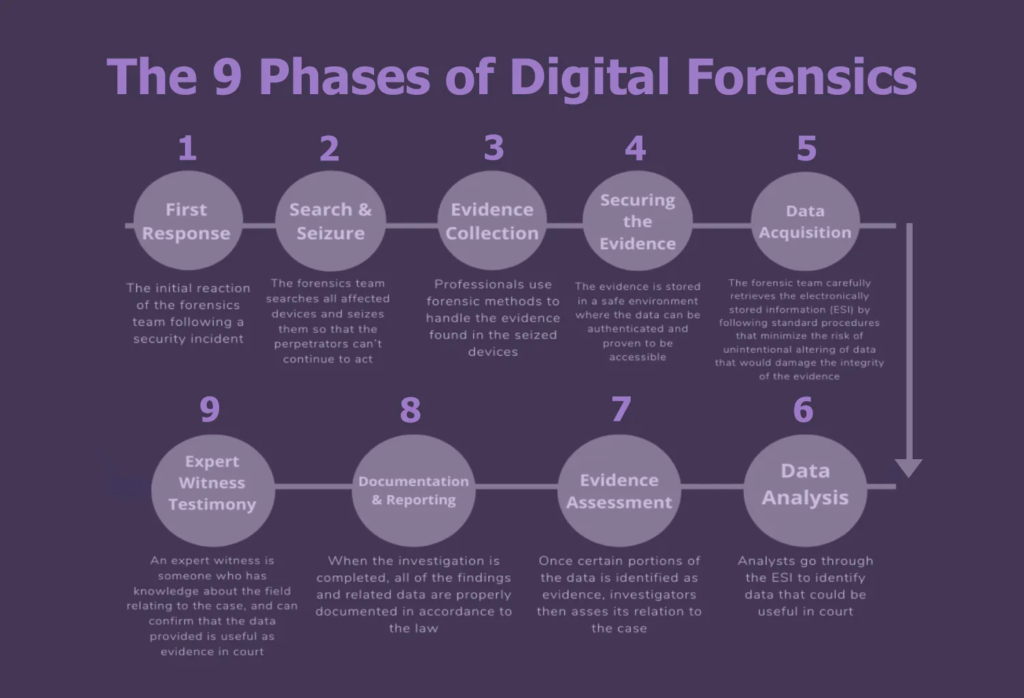
Performance Criteria
To be competent, you must be able to:
PC1. obtain items relevant to forensic examinations in line with investigative procedures from authorised channels
PC2. check forensic items against records and identify and address any inaccuracies
PC3. identify and obtain necessary resources that could be required for extracting relevant data or information from the evidences
PC4. create an image or copy of the original storage device using clean storage media to have a backup
PC5. install write blocking software to prevent any change to the data on the device or media
PC6. identify data that is required to be extracted and most likely sources
PC7. select the best method and tools for extraction as per the make and model of device
PC8. locate the required files and electronic data manually or using forensic tools
PC9. display the contents of slack space with hex editors or special slack recovery tools
PC10. hunt for files and information that have been hidden, deleted or lost
PC11. identify the type of data stored in many files by looking at their file headers or simple histogram
PC12. identify presence of encrypted data or the use of steganography and the feasibility of decryption or extracting embedded data
PC13. identify the encryption method by examining the file header, identifying encryption programs installed on the system, or finding encryption keys
PC14. extract the embedded data by finding the stego key, or by using brute force and cryptographic attacks to determine a password
PC15. crack, disable or bypass passwords placed on individual files, as well as OS passwords using various utilities and techniques
PC16. find, recover and copy data from disks that may have been hidden, encrypted or damaged, etc.
PC17. uncompress files and read disk images
PC18. extract data and metadata from files using forensic toolkits
PC19. identify malicious activity against OSs using security applications, such as file integrity checkers and host IDSs, etc.
PC20. perform string searches and pattern matching using searching tools that use Boolean, fuzzy logic, synonyms and concepts, stemming, and other search methods
PC21. assess and extract network traffic data with the goal of determining what happened and how the organization’s systems and networks have been af
fected
PC22. obtain relevant information from ISP and cloud service provider after taking due authorisation from Law Enforcement Authority/Agency
PC23. reveal (unlock) digital images that have been altered to mask the identity of a place or person
PC24. submit the device or original media for physical evidence examination after removing the data
PC25. when equipment is damaged, dismantle and rebuild the system in order to recover lost data
PC27. identify and minimise any risks to safety linked to working with forensic items in line with health and safety procedures
PC28. take measures to ensure preservation of physical evidence like finger prints, DNA etc. while handling the evidence
. Organizational
Context
KA1. relevant legislation, standards, policies, and procedures followed in the company
KA2. organization’s knowledge base and how to access and update this
KA3. the organizational systems, procedures and tasks/checklists within the domain and how to use these
KA4. the operating procedures that are applicable to the system(s) being used or task
KA5. organization’s network architecture and the IP addresses used by critical assets
KA6. organization’s typical patterns of usage on systems and networks
KA7. typical response times and service times related to own work area
KA8. limits of own responsibility and level of competence required
Technical
Knowledge
You need to know and understand:
KB1. guidelines and applicable standards for seizing and recording electronic evidence sources
KB2. usage of tools for gathering and presenting network traffic data and their limitations
KB3. networking principles
KB4. common network and application protocols and security products
KB5. network-based threats and attack methods
KB6. network traffic data sources
KB7. intrusion detection signature documentation
KB8. characteristics and relative value of all network traffic data sources so that relevant data can be located
KB9. techniques needed for analyzing data and drawing conclusions
KB10. basic steps of the examination and analysis processes
KB11. various approaches and tools to examining and analyzing network traffic data
and their limitations
KB12. data carving tools and techniques (e.g., Foremost)
KB13. binary analysis tools
KB14. common forensic tool configuration and support applications
KB15. debugging procedures and tools
KB16. basic concepts and practices of processing digital forensic data
KB17. various encryption algorithms
KB18. how to take data backup or make copies of data sources, types of backups
KB19. data recovery concepts and tools
KB20. server and client operating systems
KB21. system and application security threats and vulnerabilities
KB22. server diagnostic tools and fault identification techniques
KB23. security event correlation tool
KB24. malware analysis tools
KB25. Internet ports, protocols and services and their usefulness
KB26. security solutions
Writing Skills
You need to know and understand how to:
SA1. document call logs, reports, task lists, and schedules with co-workers
SA2. prepare status and progress reports
SA3. write memos and e-mail to customers, co-workers, and vendors to provide them with work updates and to request appropriate information without English language errors regarding grammar or sentence construct and following professional etiquettes
Reading Skills
You need to know and understand how to:
SA4. read about new products and services with reference to the organization and also from external forums such as websites and blogs
SA5. keep abreast with the latest knowledge by reading brochures, pamphlets, and product information sheets
SA6. read comments, suggestions, and responses to Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) posted on the helpdesk portal
SA7. read policy manual, standard operating procedures and service level agreements relevant to work area
SA8. read emails received from own team, across team and external vendors and clients
Oral Communication (Listening and Speaking skills)
You need to know and understand how to:
SA9. discuss task lists, schedules, and work-loads with co-workers
SA10. give clear instructions to specialists/vendors/users/clients as required
SA11. keep stakeholders informed about progress
SA12. avoid using jargon, slang or acronyms when communicating with a customer, unless it is required
SA13. receive and make phone calls, including call forward, call hold, and call mute
. Professional Skills
Decision Making

You need to know and understand how to:
SB1. follow rule-based decision-making processes
SB2. make decisions on suitable courses of action
Plan and Organize
You need to know and understand how to:
SB3. plan and organize your work to achieve targets and deadlines
Customer Centricity
You need to know and understand how to:
SB4. carry out rule-based transactions in line with customer-specific guidelines,
SB5. procedures, rules and service level agreements
SB6. check your own and/or your peers work meets customer requirements
Problem Solving
You need to know and understand how to:
SB7. apply problem-solving approaches in different situations
SB8. seek clarification on problems from others
Analytical Thinking
You need to know and understand how to:
SB9. analyze data and activities
SB10. configure data and disseminate relevant information to others
SB11. pass on relevant information to others
Critical Thinking
You need to know and understand how to:
SB12. provide opinions on work in a detailed and constructive way
SB13. apply balanced judgments to different situations
Technical Skills
You need to know and understand how to:
SC1. analyze the system architecture and design
SC2. evaluate operating system and file system configurations
SC3. configure networking and security devices
SC4. manage backups and storages
SC5. deploy and configure application systems
SC6. use word processors, spreadsheets and presentations
SC7. stay abreast of the latest developments as per industry standards and security tools to ensure that corporate security methods and tools

Analyze information or data extracted from digital forensic evidences:
Performance Criteria
To be competent, you must be able to:
PC1. identify and obtain necessary resources that could be required for examining and analysing of forensic evidences
PC2. perform analysis of the extracted data using various forensic tools
PC3. review the time and date stamps contained in the file system metadata to link files of interest to the timeframes relevant to the investigation
PC4. review system and application logs for relevant information
PC5. correlate file headers to the corresponding file extensions to identify any mismatches
PC6. perform data hiding analysis for detecting and recovering data and may indicate knowledge, ownership, or intent
PC7. analyse programs and files in various ways to provide insight into the capability of the system and the knowledge of the user
PC8. analyse file metadata typically through the application that created it to provide insight into detailed information like authorship, time last edited, number of times edited, and print or saved location, etc.
PC9. determine ownership and knowledgeable possession of the questioned data
using various methods
PC10. analyze network traffic data with the goal of determining what has happened and how the organization’s systems and networks have been affected
PC11. analyse mobile phone records to trace devices to a particular location (or to rule them out)
PC12. follow electronic data trails to uncover links between individuals or groups
PC13. piece together strings of interactions that provide a picture of activity using evidence collected from other sources than electronic devices
PC14. identify additional systems/networks compromised by cyber attacks
PC15. identify the most important characteristics of the activity and the negative impact it has caused or may cause the organization
PC16. perform computer network defence (CND) incident triage, to include determining scope, urgency, and potential impact; identifying the specific vulnerability; and making recommendations that enable expeditious remediation
PC17. perform various types of forensics analysis as per the requirement of media type, data or constraints
PC18. perform virus scanning on digital media
PC19. fuse computer network attack analyses with criminal and counterintelligence investigations and operations
PC20. identify elements of proof of the crime
PC21. identify outside attackers accessing the system from the internet or insider attackers, that is, authorized users attempting to gain and misuse non-authorized privileges
PC22. follow investigation procedure in order to determine the identity of attacker
PC23. take appropriate action to safeguard the device and relevant information for the application of physical forensic examinations
PC24. carefully document each stage of the investigation
PC25. identify risks to safety linked to working with forensic items and take the necessary actions to minimise the risks
Organizational
Context
You need to know and understand:
KA1. relevant legislation, standards, policies, and procedures followed in the company
KA2. organization’s knowledge base and how to access and update this
KA3. the organizational systems, procedures and tasks/checklists within the domain and how to use these
KA4. the operating procedures that are applicable to the system(s) being used
KA5. organization’s network architecture and the IP addresses used by critical
assets
KA6. organization’s typical patterns of usage on systems and networks
KA7. typical response times and service times related to own work area
KA8. limits of own responsibility and level of competence required
Technical
Knowledge
You need to know and understand:
KB1. guidelines and applicable standards for examining and analysing electronic evidence sources
KB2. usage of tools for gathering and presenting network traffic data and their limitations
KB3. networking principles
KB4. basic steps of the examination and analysis processes
KB5. various analysis approaches and techniques and their application
KB6. legal and technical limitations to various analysis approaches and techniques
KB7. common network and application protocols and security products
KB8. network-based systems and application threats and attack methods
KB9. intrusion detection signature documentation
KB10. characteristics and relative value of all network traffic data sources so that relevant data can be located
KB11. techniques needed for analyzing data and drawing conclusions
KB12. data carving tools and techniques (e.g., Foremost)
KB13. binary analysis tools and their application
KB14. common forensic tool configuration and support applications
KB15. debugging procedures and tools
KB16. basic concepts and practices of processing digital forensic data
KB17. various encryption algorithms
KB18. how to take data backup, types of backups and recovery concepts and tools
KB19. server and client operating systems
KB20. server diagnostic tools and fault identification techniques
KB21. security event correlation tools
KB22. malware analysis tools
KB23. internet ports, protocols and services and their usefulness
KB24. security solutions
Writing Skills
You need to know and understand how to:
SA1. document call logs, reports, task lists, and schedules with co-workers
SA2. prepare status and progress reports
SA3. write memos and e-mail to customers, co-workers, and vendors to provide them with
work updates and to request appropriate information without English language errors regarding grammar or sentence construct and following professional etiquettes
Reading Skills
You need to know and understand how to:
SA4. read about new products and services with reference to the organization and also from external forums such as websites and blogs
SA5. keep abreast with the latest knowledge by reading brochures, pamphlets, and product information sheets
SA6. read comments, suggestions, and responses to Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) posted on the helpdesk portal
SA7. read policy manual, standard operating procedures and service level agreements relevant to work area
SA8. read emails received from own team, across team and external vendors and clients
Oral Communication (Listening and Speaking skills)
You need to know and understand how to:
SA9. discuss task lists, schedules, and work-loads with co-workers
SA10. give clear instructions to specialists/vendors/users/clients as required
SA11. keep stakeholders informed about progress
SA12. avoid using jargon, slang or acronyms when communicating with a customer, unless it is required
SA13. receive and make phone calls, including call forward, call hold, and call mute
. Professional Skills
Decision Making
You need to know and understand how to:
SB1. follow rule-based decision-making processes
SB2. make decisions on suitable courses of action
Plan and Organize
You need to know and understand how to:
SB3. plan and organize your work to achieve targets and deadlines
Customer Centricity
You need to know and understand how to:
SB4. carry out rule-based transactions in line with customer-specific guidelines,
SB5. procedures, rules and service level agreements
SB6. check your own and/or your peers work meets customer requirements
Problem Solving
You need to know and understand how to:
SB7. apply problem-solving approaches in different situations
SB8. seek clarification on problems from others
Analytical Thinking
You need to know and understand how to:
SB9. analyze data and activities
SB10. configure data and disseminate relevant information to others
SB11. pass on relevant information to others
Critical Thinking
You need to know and understand how to:
SB12. provide opinions on work in a detailed and constructive way
SB13. apply balanced judgments to different situations
Technical Skills
You need to know and understand how to:
SC1. analyze the system architecture and design
SC2. evaluate operating system and file system configurations
SC3. configure networking and security devices
SC4. manage backups and storages
SC5. deploy and configure application systems
SC6. use word processors, spreadsheets and presentations
SC7. stay abreast of the latest developments as per industry standards and security tools to ensure that corporate security methods and tools

Report and present the results of a forensic investigation:
Performance Criteria
To be competent, you must be able to:
PC1. identify and obtain necessary resources that could be required for reporting and presenting forensic investigation, its results and evidences
PC2. ensure all relevant information is collated and captured in the report accurately and clearly
PC3. list and organise for supporting materials that are included with the report,
such as printouts of particular items of evidence, digital copies of evidence, chain of
custody documentation, photos, emails (showing email headers, the path and timing emails took to get from source to destination), etc.
PC4. create a brief summary of the results of the examinations performed on the items submitted for analysis
PC5. provide comprehensive details of findings in the report
PC6. create a glossary with the report to assist the reader using an accepted source
for the definition of the terms and include appropriate references
PC7. ensure that the evidence remains pristine and unaltered while presenting
PC8. present and explain track record of information exchange, and the also referred to as a checksum, as a mark of authenticity
PC9. carefully document each stage of your investigation
PC10. work within the level of authority and expertise taking actions necessary should these be exceeded
PC11. differentiate between fact and opinion and express opinions within your area of expertise while writing the report
PC12. identify any risks to safety linked to working with forensic items in line with health and safety procedures
PC13. take the necessary actions to minimize any risks linked to working with forensic items
PC14. take appropriate action to safeguard the device and relevant information for the application of physical forensic examinations
PC15. take appropriate action to ensure confidentiality and integrity of report and related documents
. Organizational
Context
KA1. relevant legislation, standards, policies, and procedures followed in the company
KA2. organization’s knowledge base and how to access and update this
KA3. the organizational systems, procedures and tasks/checklists within the domain and how to use these
KA4. the operating procedures that are applicable to the system(s) being used
KA5. organization’s network architecture and the IP addresses used by critical assets
KA6. organization’s typical patterns of usage on systems and networks
KA7. typical response times and service times related to own work area
KA8. limits of own responsibility and level of competence required
Technical
Knowledge
You need to know and understand:
KB1. the implications of current law, policies, operating procedures and guidelines
relevant to the evaluation and interpretation of forensic materials
KB2. the type, extent and purpose of reports regarding forensic examinations
KB3. the established scientific and forensic principles and practices on which to base conclusions
KB4. how to assimilate different opinions and propositions in order to formulate
conclusions within area of expertise
KB5. the principles involved in processing, evaluating and interpreting results of examinations, and the importance of considering probability and statistical variation
KB6. comparison and evaluation methods and techniques used in forensic examinations
KB7. limitations of examinations used, and the importance of expressing these limitations
KB8. current opinions on working practice in forensic sampling and evaluation relevant to area of operations
KB9. when and how to consider alternative propositions, and how these might be tested
KB10. the importance of recognizing the limitations of your own abilities and to consult with others where necessary
KB11. how to ensure that information used is current, reliable and accurate
KB12. the principal types of stakeholders and their different requirements from forensic examination processes
KB13. the importance of communicating to the needs of the audience
KB14. methods used to present technical explanations to facilitate
KB15. understanding by stakeholders, including non-scientists
KB16. methods for checking understanding between relevant parties when communicating
KB17. the importance of clarifying areas of agreement and disagreement, and methods for doing this
KB18. the importance of impartiality and how to present balanced opinions and conclusions
KB19. the importance of ensuring that findings and conclusions you provide are consistent with written reports, statements or other documentation
KB20. techniques needed for analyzing data and drawing conclusions
KB21. basic steps of the examination and analysis processes
KB22. various approaches and tools to examining and analyzing network traffic data and their limitations
KB23. basic concepts and practices of processing digital forensic data
Writing Skills
You need to know and understand how to:
SA1. document call logs, reports, task lists, and schedules with co-workers
SA2. prepare status and progress reports
SA3. write memos and e-mail to customers, co-workers, and vendors to provide them with work updates and to request appropriate information without English language errors regarding grammar or sentence construct and following professional etiquettes
Reading Skills
You need to know and understand how to:
SA4. read about new products and services with reference to the organization and also from external forums such as websites and blogs
SA5. keep abreast with the latest knowledge by reading brochures, pamphlets, and product information sheets
SA6. read comments, suggestions, and responses to Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) posted on the helpdesk portal
SA7. read policy manual, standard operating procedures and service level agreements relevant to work area
SA8. read emails received from own team, across team and external vendors and clients
Oral Communication (Listening and Speaking skills)
You need to know and understand how to:
SA9. discuss task lists, schedules, and work-loads with co-workers
SA10. give clear instructions to specialists/vendors/users/clients as required
SA11. keep stakeholders informed about progress
SA12. avoid using jargon, slang or acronyms when communicating with a customer, unless it is required
SA13. receive and make phone calls, including call forward, call hold, and call mute
Professional Skills
Decision Making
You need to know and understand how to:
SB1. follow rule-based decision-making processes
SB2. make decisions on suitable courses of action
Plan and Organize
You need to know and understand how to:
SB3. plan and organize your work to achieve targets and deadlines
Customer Centricity
You need to know and understand how to:
SB4. carry out rule-based transactions in line with customer-specific guidelines,
SB5. procedures, rules and service level agreements
SB6. check your own and/or your peers work meets customer requirements
Problem Solving
You need to know and understand how to:
SB7. apply problem-solving approaches in different situations
SB8. seek clarification on problems from others
Analytical Thinking
You need to know and understand how to:
SB9. analyze data and activities
SB10. configure data and disseminate relevant information to others
SB11. pass on relevant information to others
Critical Thinking
You need to know and understand how to:
SB12. provide opinions on work in a detailed and constructive way
SB13. apply balanced judgments to different situations
Technical Skills
You need to know and understand how to:
SC1. work on various operating systems
SC2. work with word processors, spreadsheets, presentations and statistical tools
SC3. stay abreast of the latest developments in terms of industry standards and information security tools and techniques
Guidelines for Assessment:
- Criteria for assessment for each Qualification Pack (QP) will be created by the Sector Skill Council (SSC). Each performance criteria (PC) will be assigned Theory and Skill/Practical marks proportional to its importance in NOS.
- The assessment will be conducted online through assessment providers authorized by SSC.
- Format of questions will include a variety of styles suitable to the PC being tested such as multiple choice questions, fill in the blanks, situational judgment test, simulation and programming test.
- To pass a QP, a trainee should pass each individual NOS. Standard passing criteria for each NOS is 70%.