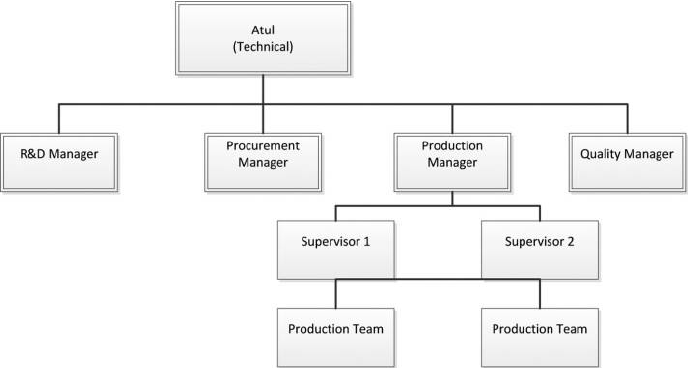
Supervisor Structure (Technical) ( 6 month course)
Supervisor Structure (Technical) click here
Brief Job Description
This job role is responsible for planning, managing and allocating resources for various structural works at
construction sites, supervising and monitoring concreting, bar bending, system shuttering carpentry and
scaffolding works and activities while ensuring observation of health safety and environmental practices at work site.

Personal Attributes
The Supervisor Structure (Technical) is expected to be physically fit to work across various locations with
varied environmental conditions. The person should be organized, diligent, methodical, safety-conscious,
and a prompt decision-maker. In addition to being a team player, the individual should have good
communication skills.
Interpret drawings, specifications and standards for structural execution
Description
This unit describes the skills and knowledge required to read and interpret architectural GFC/ shop
drawings, specifications and standards for structural execution
Scope
The scope covers the following :
Interpret drawings, specifications and standards for concreting, scaffolding, shuttering carpentry and
bar bending and steel fixing operations
Elements and Performance Criteria
Interpret drawings, specifications and standards for concreting, scaffolding, shuttering carpentry and bar
bending and steel fixing operations
To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to:
PC1. interpret details from Architectural GFC/ Shop drawings
PC2. interpret details from schedule of work
PC3. interpret specification and standards provided for relevant works
PC4. interpret all specification provided in the relevant drawing
PC5. interpret schedule provided for completion of work
PC6. read method statement for execution of work
PC7. interpret manufactures specification for operation of power tools
PC8. carry out calculation of required quantity of materials from relevant schematic working
drawings
PC9. reproduce technical drawings as simplified hand sketches for explaining and providing
clear instructions to subordinates
Knowledge and Understanding (KU)
The individual on the job needs to know and understand:
KU1. standard practices for structural works
KU2. safety rules and regulations for handling and storing relevant tools, equipment, and
materials required for relevant works in accordance with organizational norms
KU3. importance of personal protection including the use of related safety gears and equipment in
accordance with organizational norms
KU4. service request procedures for tools, materials and equipment as per organizational norms
KU5. procedure for maintenance of tools and equipment
KU6. statutory compliance requirement related to workmen engagement
KU7. schematic drawings, sketches for relevant work
KU8. principless involved in reading and interpreting various relevant drawings
KU9. how to read general arrangement drawing
KU10. simplified sketch preparation from the drawing
KU11. how to read plan, elevation and sectional drawing
KU12. basic principal of measurement, arithmetic and geometric calculations
KU13. terminology used in concreting, scaffolding, bar-bending and shuttering carpentry works
KU14. linear conversion of units
KU15. manufacturers specification and work method statement for relevant works
KU16. how to calculate material and resource required for relevant works
KU17. work method statement and scope of work
KU18. calculation of required quantity of materials from relevant schematic working drawings
Generic Skills (GS)
User/individual on the job needs to know how to:
GS1. write in at least one language, preferably in the local language of the site
GS2. read sketches, instructions provided for the work, and various signboards, safety rules,
safety tags, exit route information in one or more languages, preferably in the local language
of the site
GS3. speak in one or more language, preferably one of the local language at the site
GS4. communicate orally and effectively with team members
GS5. analyze the safety aspect of the workplace
GS6. plan work and organize required resource effectively
GS7. complete work as per agreed time schedule and quality parameters
GS8. resolve any conflict within the teammates
GS9. evaluate the complexity of the tasks
GS10. identify any violation of safety norms during the work
Plan, supervise and monitor execution of system shuttering carpentry works
Description
This unit describes the skills and knowledge required to plan, allocate resources and supervise and monitor execution of system shuttering carpentry works.

Scope
The scope covers the following :
Plan and allocate resources for shuttering carpentry works
Procure approvals and prepare checklist prior to and after commencement of work.
Supervise and ensure execution of system shuttering carpentry works in accordance with agreed
work plan
Elements and Performance Criteria
Plan and allocate resources for shuttering carpentry works
To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to:
PC1. interpret drawings, specification and standards for formwork
PC2. confirm work hours and requirement for shuttering carpentry works with concerned superior
PC3. calculate component wise requirement for formwork
PC4. calculate the requirement of tools, tackles, consumables, equipment and manpower for
making and erection of formwork
PC5. determine method of lifting, route and mode of transportation of relevant materials
PC6. allocate manpower and ensure their productivity
Procure approvals and prepare checklist prior to and after commencement of work
To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to:
PC7. notify concerned superior for resources and equipment requirement
PC8. take safety clearance from services and EHS department before commencing shuttering
work
PC9. provide clearance and mobility order to subcontractors for mobilization of resource and
material at next workspace
PC10. check for completion of preparatory activities and coordinate between various departments
PC11. carry out checks and fill checklist after completion of work
PC12. provide status information on work received, in progress, backlog, and work assignments
completed as requirement
PC13. maintain records and files and prepare reports on labour deployment, work done and
productivity
PC14. review estimates, prepares sketches and reports on labor expenditures and materials used
Supervise and ensure execution of system shuttering carpentry works in accordance with agreed work
plan
To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to:
PC15. assist in sequencing key activities related to shuttering carpentry works for making schedule
PC16. assist in planning of timeline for identified key activities
PC17. record carpenters’ time and materials used for each job
PC18. supervise carpentry jobs requiring a high degree of skill
PC19. ensure survey works and preparatory works are complete so as to provide required level &
reference
PC20. check and ensure quality of plywood & timber prior to use
PC21. ensure availability of all tools, components, materials and fixture for assembling of shutters
PC22. ensure shutter is fabricated as per workshop drawing
PC23. ensure erected formwork is as per specified standards
PC24. ensure that appropriate procedure is followed while erecting formwork and while installing
necessary supports, braces, penetrations, embedded parts, etc.
PC25. check provision for lifting arrangement are provided in case of lifting of heavy weight
formwork
PC26. monitor installation of jump form system using cranes or hydraulic system
PC27. monitor operation of jump form system
PC28. monitor proper functioning of hydraulic jack and cranes
PC29. monitor rising of formwork using hydraulic jacks and cranes
PC30. ensure safe lifting and lowering of formwork material using cranes
PC31. ensure that formwork is dismantled sequentially and safety following manufacturers
instructions/ specification
PC32. provide assistance on complex jobs and ensure proper erection and dismantling of shuttering
and formwork system
Knowledge and Understanding (KU)
The individual on the job needs to know and understand:
KU1. standard practices for shuttering and formwork for in situ and pre cast construction works
KU2. safety rules and regulations for handling and storing relevant tools, equipment, and
materials required for relevant works in accordance with organizational norms
KU3. importance of personal protection including the use of related safety gears and equipment in
accordance with organizational norms
KU4. service request procedures for tools, materials and equipment as per organizational norms
KU5. procedure for maintenance of tools and equipment
KU6. statutory compliance requirement related to workmen engagement
KU7. trade productivity norms
KU8. use of compact laser devices for setting out
KU9. company policies and hierarchy for reporting any anomaly
KU10. writing reports for submission to concerned authority
KU11. process of indent
KU12. determine work methods which makes best use of relevant resource
KU13. documentation required for resource management such as preparation of indents, material
and manpower calculation, preparation of daily labor reports
KU14. providing mobilization order to sub-contractors
KU15. various checklist for pre-approval and post clearance of work
KU16. optimum utilization and allocation of tools, equipment and resources as per requirement
KU17. how to calculate productivity
KU18. procedure for fixing of components for making shutters
KU19. terminology used in formwork
KU20. different types and sizes of formwork material
KU21. unit weight of individual formwork components
KU22. equipment’s to be used for lifting of formwork material
KU23. lifting capacity of belts, slings etc.
KU24. procedure adopted for lifting of assembled shutters
KU25. reconciliation of materials used for making shutters
KU26. how to control wastage of materials
KU27. detailed working knowledge of any of the following formwork systems, RMD, TRAD, Peri And
Doka systems
KU28. how to use tools and equipment common to the shuttering carpentry
KU29. sequence and prioritizing of activities
KU30. how to identify priority and critical activity of relevant task
KU31. functional of hydraulic system
KU32. how to check plumb and take corrective action
KU33. how to determine & control rotation
KU34. use of fixtures, connection
KU35. use of tools, tackles, components and equipment required for installation and operation of
climbing formwork
KU36. types of formwork and their applications for basic and complex structures
KU37. types of cranes and hydraulic jacks used for lifting of climbing formwork
Generic Skills (GS)
User/individual on the job needs to know how to:
GS1. write in at least one language, preferably in the local language of the site
GS2. read sketches, instructions provided for the work, and various signboards, safety rules,
safety tags, exit route information in one or more languages, preferably in the local language
of the site
GS3. speak in one or more language, preferably one of the local language at the site
GS4. communicate orally and effectively with team members
GS5. analyze the safety aspect of the workplace
GS6. plan work and organize required resource effectively
GS7. complete work as per agreed time schedule and quality parameters
GS8. resolve any conflict within the teammates
GS9. evaluate the complexity of the tasks
GS10. identify any violation of safety norms during the work
Plan, supervise and monitor execution of concreting works
Description
This unit describes the skills and knowledge required to supervise and monitor execution of concreting
works
Scope
The scope covers the following :
Plan and allocate resources for concreting works
Procure approvals and prepare checklist prior to and after commencement of concreting work.
Supervise and ensure execution of concreting works in accordance with agreed work plan
Elements and Performance Criteria
Plan and allocate resources for concreting works
To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to:
PC1. interpret drawings, specification and standards for concreting work
PC2. confirm work hours and requirement for concreting works with concerned superior
PC3. calculate the requirement of tools, tackles, consumables, equipment and manpower for
concreting work
PC4. determine method of lifting, route and mode of transportation of relevant materials from
mixing point to pouring point
PC5. allocate manpower and ensure their productivity
Procure approvals and prepare checklist prior to and after commencement of concreting work
To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to:

PC6. notify concerned superior for resources and equipment requirement
PC7. take safety clearance from services and EHS department before commencing concreting
work
PC8. provide clearance and mobility order to subcontractors for mobilization of resource and
material at next workspace
PC9. check for completion of preparatory activities and coordinate between various departments
PC10. carry out checks and fill checklist after completion of work
PC11. provide status information on work received, in progress, backlog, and work assignments
completed as requirement
PC12. maintain records and files and prepare reports on labour deployment, work done and
productivity
PC13. review estimates, prepares sketches and reports on labor expenditures and materials used
Supervise and ensure execution of concreting works in accordance with agreed work plan
To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to:
PC14. inspect work progress, equipment, or construction sites to verify safety or to ensure that
specifications are met
PC15. record information such as personnel, production, or operational data on specified forms or
reports
PC16. coordinate with batching plant and construction site confirming continuity of supply of
concrete
PC17. interpret specification sheets for information, such as sizes of aggregates and proportions of
cement and water required, to ensure that concrete is mixed according to specifications
PC18. inspect bracing and shoring of concrete forms to ensure their stability before and during
pouring
PC19. inspect the fixing and setting of pump line ,machinery for pouring of concrete
PC20. record details of the concreting works covering grade of concrete, area and volume of pour,
number of workers ,tools and equipment deployed for work and achieved productivity
PC21. indicates positions for pouring chutes and runways, cranes, or paving machines to facilitate
conveying concrete from mixer to forms
PC22. directs workers who spread, vibrate, screed, and float concrete to ensure that concrete is
compacted to desired consistency and surface is finished to specified uniformity and
smoothness
PC23. check for bulking and loose formwork during concreting
PC24. ensure execution of concreting in extreme hot/cold weather as per standard practices and
specification
PC25. examines concrete, after forms are stripped, and gives instruction to workers to repair
defects, such as roughness and honeycombed appearance
PC26. prescribe methods for curing concrete, such as covering surface of green (fresh) concrete
with burlap, plastic, earth, straw, or chemical compound, to prevent green concrete from
drying out rapidly or freezing
Knowledge and Understanding (KU)
The individual on the job needs to know and understand:
KU1. standard practices for concreting works
KU2. safety rules and regulations for handling and storing relevant tools, equipment, and
materials required for relevant works in accordance with organizational norms
KU3. importance of personal protection including the use of related safety gears and equipment in
accordance with organizational norms
KU4. service request procedures for tools, materials and equipment as per organizational norms
KU5. procedure for maintenance of tools and equipment
KU6. statutory compliance requirement related to workmen engagement
KU7. trade productivity norms
KU8. use of compact laser devices
KU9. company policies and hierarchy for reporting any anomaly
KU10. writing reports for submission to concerned authority
KU11. process of indent
KU12. determine work methods which makes best use of relevant resource
KU13. documentation required for resource management such as preparation of indents, material
and manpower calculation, preparation of daily labor reports
KU14. providing mobilization order to sub-contractors
KU15. various checklist for pre-approval and post clearance of work
KU16. optimum utilization and allocation of tools, equipment and resources as per requirement
KU17. how to calculate productivity
KU18. how to measure and check lines and levels for maintaining layout and alignment
KU19. standard practices, materials, and methods of the concreting works
KU20. use of tools and equipment for concreting works
KU21. structural drawings relevant to concreting works
KU22. methodology for estimation of required resource and material
KU23. standard tolerance levels for all aspects of concreting work (including pouring, screening,
leveling and finishing)
KU24. difference and comparison between pre cast and in situ concreting works
KU25. basic properties and mix proportions of concrete
KU26. basic properties and mix proportions of concrete
KU27. appropriate techniques (including use of tools, equipment and material) for all aspects of
concreting work (including pouring, screening, leveling and finishing)
KU28. methodology for checking line ,level and alignment for various concreting works
KU29. methodology of concreting works in horizontal, vertical and inclined surfaces
KU30. different type of high quality concrete finish
KU31. sequence of pour
KU32. variation of slump w.r.t rate of pour
KU33. different type of vibrators used(internal/external vibrators),their accessibility and influence
area
KU34. vibration in congested areas
KU35. construction joints/cold joints
KU36. curing technique of form finished concrete
KU37. self-compact concrete
KU38. initial, final setting of concrete and their checking
KU39. correct positioning of the pump hose when pumping the SCC
KU40. methodology for hot/cold weather concreting works
KU41. major risks associated with hot and cold weather concrete

Generic Skills (GS)
User/individual on the job needs to know how to:
GS1. write in at least one language, preferably in the local language of the site
GS2. read sketches, instructions provided for the work, and various signboards, safety rules,
safety tags, exit route information in one or more languages, preferably in the local language
of the site
GS3. speak in one or more language, preferably one of the local language at the site
GS4. communicate orally and effectively with team members
GS5. analyze the safety aspect of the workplace
GS6. plan work and organize required resource effectively
GS7. complete work as per agreed time schedule and quality parameters
GS8. resolve any conflict within the teammates
GS9. evaluate the complexity of the tasks
GS10. identify any violation of safety norms during the work
Plan, supervise and monitor execution of bar bending works
Description
This unit describes the skills and knowledge required to supervise and monitor execution of concreting
works
Scope
The scope covers the following :
Plan and allocate resources for bar bending works
Procure approvals and prepare checklist prior to and after commencement of work.
Supervise and ensure execution of bar-bending works in accordance with agreed work plan
Elements and Performance Criteria
Plan and allocate resources for bar bending works
To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to:
PC1. interpret drawings, specification and standards for bar bending works
PC2. confirm work hours and requirement for bar bending works with concerned superior
PC3. calculate the requirement of tools, tackles, consumables, equipment and manpower for bar
bending works
PC4. determine method of lifting, route and mode of transportation of relevant materials from
stock yard to erection point
PC5. allocate manpower and ensure their productivity
Procure approvals and prepare checklist prior to and after commencement of work
To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to:
PC6. notify concerned superior for resources and equipment requirement
PC7. take safety clearance from services and EHS department before commencing bar bending
work
PC8. provide clearance and mobility order to subcontractors for mobilization of resource and
material at next workspace
PC9. check for completion of preparatory activities and coordinate between various departments
PC10. carry out checks and fill checklist after completion of work
PC11. provide status information on work received, in progress, backlog, and work assignments
completed as requirement
PC12. maintain records and files and prepare reports on labor deployment, work done and
productivity
PC13. review estimates, prepares sketches and reports on labor expenditures and materials used
Supervise and ensure execution of bar-bending works in accordance with agreed work plan
To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to:
PC14. supervise bar bending task requiring high degree of skill
PC15. inspect work progress, equipment, or construction sites to verify safety or to ensure that
specifications are met
PC16. record information such as personnel, production, or operational data on specified forms or
reports
PC17. read and follow manufactures specification for operation of power tools and CNC machine for
cutting and bending
PC18. carry out weighing of steel reinforcement before unloading at site in coordination with the
stores
PC19. ensure standard practices for storing and stacking of reinforcement steel at the yard
PC20. monitor all reinforcement bars cutting and bending activity at yard
PC21. ensure bundling/tagging and stacking of cut and bent bars as per bar marking the BBS
PC22. ensure scaffolding is complete as per required / specified heights/requirements, method,
load carrying capacity, etc.
PC23. check and ensure use of approved BBS for execution of reinforcement work
PC24. optimize use of already available cut steel rods to minimize wastage
PC25. plan sequence of insertion and fixing of reinforcement bars for different types of structures
PC26. co-relate the sequence of reinforcement placing with fixing of inserts, sleeves, conduits and
anchors
PC27. check quality of mechanical connections of reinforcement bars
PC28. check the quality of pre-fabricated reinforcement cage and the erection process
PC29. ensure reinforcement bars, cast-in items, corrugated sleeve pipes, recesses, lifting hooks
and inserts are correctly positioned and properly secured, within specified tolerance levels
PC30. ensure that the joints and edges of the mold, bolts, stoppers, tie rods, side props and
rubber seal are intact and properly secured
PC31. check for stiffening of cage before lifting for stacking/erection
PC32. ensure completion of bar bending works as per agreed time schedule and within applicable
tolerance limits
Knowledge and Understanding (KU)
The individual on the job needs to know and understand:
KU1. standard practices for reinforcement works
KU2. safety rules and regulations for handling and storing relevant tools, equipment, and
materials required for relevant works in accordance with organizational norms
KU3. importance of personal protection including the use of related safety gears & equipment in
accordance with organizational norms
KU4. service request procedures for tools, materials and equipment as per organizational norms
KU5. procedure for maintenance of tools and equipment
KU6. statutory compliance requirement related to workmen engagement
KU7. trade productivity norms
KU8. use of compact laser devices
KU9. company policies and hierarchy for reporting any anomaly
KU10. writing reports for submission to concerned authority
KU11. determine work methods which makes best use of relevant resource
KU12. documentation required for resource management such as preparation of indents, material
and manpower calculation, preparation of daily labor reports
KU13. providing mobilization order to sub-contractors
KU14. various checklist for pre-approval and post clearance of work
KU15. optimum utilization and allocation of tools, equipment and resources as per requirement
KU16. how to calculate productivity
KU17. standard procedures for stacking of reinforcement
KU18. various types of steel such as mild steel , tor steel and TMT steel
KU19. method to prevent reinforcement against rusting, and weathering effect
KU20. bundling and tagging of reinforcement bars

KU21. schematic drawings, sketches and BBS
KU22. how to operate hand tools, power tools, CNC machine for their respective applications in
reinforcement work
KU23. types of mechanical couplers and manufacturers instructions for their installations
KU24. types and optimum use of binding wire
KU25. common terminology used in reinforcement works
KU26. corrective measure for reinforcement
KU27. method for fixing of mechanical coupler
KU28. max allowable wastage of reinforcement bars
KU29. basic reconciliation of reinforcement
KU30. rolling marking of reinforcement
KU31. unit weight of reinforcement bars of different diameter
KU32. tolerance limits for various types of reinforcement works as per Indian/international codes
KU33. importance of reinforcement in precast RCC works
KU34. reinforcement insertion procedures for special structures like arches, domes, etc.
Generic Skills (GS)
User/individual on the job needs to know how to:
GS1. write in at least one language, preferably in the local language of the site
GS2. read sketches, instructions provided for the work, and various signboards, safety rules,
safety tags, exit route information in one or more languages, preferably in the local language
of the site
GS3. speak in one or more language, preferably one of the local language at the site
GS4. communicate orally and effectively with team members
GS5. analyze the safety aspect of the workplace
GS6. plan work and organize required resource effectively
GS7. complete work as per agreed time schedule and quality parameters
GS8. resolve any conflict within the teammates
GS9. evaluate the complexity of the tasks
GS10. identify any violation of safety norms during the work
Plan, supervise and monitor execution of scaffolding works
Description
This unit describes the skills and knowledge required to supervise and monitor execution of scaffolding
works.
Scope
The scope covers the following :
Plan and allocate resources for scaffolding works
Procure approvals and prepare checklist prior to and after commencement of work.
Supervise and ensure execution of scaffolding works in accordance with agreed work pla
Elements and Performance Criteria
Plan and allocate resources for scaffolding works
To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to:
PC1. interpret drawings, specification and standards for scaffolding works
PC2. confirm work hours and requirement for scaffolding works with concerned superior
PC3. calculate quantity of various components for scaffolding
PC4. calculate the requirement of tools, tackles, consumables, equipment and manpower for bar
bending works
PC5. determine method of lifting, route and mode of transportation of relevant materials from
stock yard to erection point
PC6. allocate manpower and ensure their productivity
Procure approvals and prepare checklist prior to and after commencement of work
To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to:
PC7. notify concerned superior for resources and equipment requirement
PC8. take safety clearance from services and EHS department before commencing scaffolding
work
PC9. provide clearance and mobility order to subcontractors for mobilization of resource and
material at next workspace
PC10. check for completion of preparatory activities and coordinate between various departments
PC11. carry out checks and fill checklist after completion of work
PC12. provide status information on work received, in progress, backlog, and work assignments
completed as requirement
PC13. maintain records and files and prepare reports on labour deployment, work done and
productivity
PC14. review estimates, prepares sketches and reports on labor expenditures and materials used
Supervise and ensure execution of scaffolding works in accordance with agreed work plan
To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to:
PC15. supervise scaffolding task requiring high degree of skill
PC16. inspect work progress, equipment, or construction sites to verify safety or to ensure that
specifications are met
PC17. record information such as personnel, production, or operational data on specified forms or
reports
PC18. ensure completion of surveying, marking and other preparatory arrangement
PC19. ensure that standard procedure is followed during erection of scaffold
PC20. ensure safe lifting and lowering of scaffold material manually or by using crane
PC21. ensure height of scaffold erected is within permissible limits
PC22. ensure all working platform are properly fixed for carrying out subsequent activity
PC23. check scaffold for rigidity and ensured stability
PC24. ensure scaffolds are used only for intended purpose
PC25. ensure maintenance of safety protocol while using or accessing scaffold
PC26. check all guardrails, toe board, walk way boards, fall protection are in place to ensure safety
PC27. check scaffold is tagged for its purpose (safe for use, unsafe for use, scaffold incomplete)
PC28. check and ensure scaffold is supported with permanent structure at regular interval as per
standard practices
PC29. check scaffold with respect to inspection checklist
PC30. record details of erected scaffold and document inspection checklist

Knowledge and Understanding (KU)
The individual on the job needs to know and understand:
KU1. standard practices for scaffolding works
KU2. safety rules and regulations for handling and storing relevant tools, equipment, and
materials required for relevant works in accordance with organizational norms
KU3. importance of personal protection including the use of related safety gears & equipment in
accordance with organizational norms
KU4. service request procedures for tools, materials and equipment as per organizational norms
KU5. procedure for maintenance of tools and equipment
KU6. statutory compliance requirement related to workmen engagement
KU7. trade productivity norms
KU8. use of compact laser devices for setting out
KU9. company policies and hierarchy for reporting any anomaly
KU10. writing reports for submission to concerned authority
KU11. process of indent
KU12. determine work methods which makes best use of relevant resource
KU13. documentation required for resource management such as preparation of indents, material
and manpower calculation, preparation of daily labor reports
KU14. providing mobilization order to sub-contractors
KU15. various checklist for pre-approval and post clearance of work
KU16. optimum utilization and allocation of tools, equipment and resources as per requirement
KU17. how to calculate productivity
KU18. scaffolding tasks
KU19. how to measure and check lines and levels for maintaining layout and alignment
KU20. standard practices, materials, and methods of the scaffolding works
KU21. use of tools and equipment common to the scaffolding trade
KU22. basic principles of measurement along with simple geometry
KU23. methodology for estimation of required resource and material
KU24. procedure for layout of scaffolding as per drawings
KU25. how to read and interpret scaffolding drawing , other relevant working drawings and working
method statement
KU26. standard tolerance limits for of scaffolding work (including erection and dismantling of
conventional scaffold, mobile tower, staircase, complex scaffolds, etc.)
KU27. safety mechanism for scaffolds in normal and confined areas
KU28. preventive and corrective action to ensure that the scaffolding work meets the quality
requirements as per drawings
KU29. checklist for scaffolding works
KU30. importance of snag list clearance
KU31. basic principle of measurement and marking
KU32. arithmetic and geometry calculation
KU33. maximum tolerance limit for scaffold as per Indian/International code practices
KU34. line, level and alignment required for scaffold
KU35. preventive and corrective action to ensure scaffold meets the required standards of quality
KU36. components, materials and tools used in scaffolding works
KU37. procedure for layout of scaffold as per drawings
KU38. different types of scaffolds system such as pipe and couplers and other common customized
system scaffold (frame scaffold ) for basic and complex structures






