Portfolio in Fashion
Introduction: A fashion portfolio is a curated collection of a designer’s work that showcases their skills, creativity, design process, and vision. It is an essential tool for fashion designers, whether they are applying for fashion school, internships, or jobs in the industry. A well-crafted portfolio not only reflects a designer’s artistic abilities but also their technical knowledge, understanding of trends, and ability to execute ideas into tangible fashion pieces.
This class note covers the purpose of a fashion portfolio, what should be included, how to structure it, tips for presenting your work effectively, and its importance in building a career in fashion.

What is a Fashion Portfolio?
A fashion portfolio is a personalized presentation of a designer’s body of work. It demonstrates their design philosophy, creativity, technical skills, and their approach to fashion. Portfolios can be either physical or digital and are tailored to the specific role or audience the designer is targeting.
In fashion, a portfolio is a visual résumé, designed to grab attention and communicate an individual’s style, skills, and thought process. It typically contains sketches, technical drawings, photos of finished garments, mood boards, fabric swatches, and even 3D models or videos if digital elements are involved.
Why is a Fashion Portfolio Important?
- Showcase of Creativity and Skill: A fashion portfolio reflects your ability to conceptualize, design, and execute fashion ideas. It gives prospective employers or educators insight into your artistic sensibility and technical know-how.
- Personal Branding: Your portfolio is a reflection of your unique aesthetic and brand as a designer. It allows you to communicate your creative identity and differentiate yourself from others in the industry.
- Professional Requirement: In most cases, a strong portfolio is required when applying to fashion schools, internships, design competitions, or fashion design jobs. It’s often the first impression you make on a potential employer.
- Demonstrating Growth: A well-curated portfolio can show the evolution of your design skills over time. By including both past and recent projects, it illustrates how you’ve developed creatively and professionally.
- Versatility and Range: A portfolio gives you the chance to show your versatility as a designer. Whether you specialize in menswear, womenswear, sustainable fashion, or accessories, your portfolio should demonstrate your range of expertise.
Key Components of a Fashion Portfolio:
- Introduction:
- Start with a brief personal statement or biography. This section should highlight your background, what inspires your designs, and your goals as a fashion designer. Make it concise yet impactful.
- Include your name, contact information, and links to any personal websites or social media relevant to your professional work.
- Mood Boards:
- Mood boards visually communicate your inspiration and the thematic elements of your collection. They may include color palettes, textures, fabrics, images, or art that inspired your designs.
- A mood board helps the viewer understand the concept and creative process behind your collection.
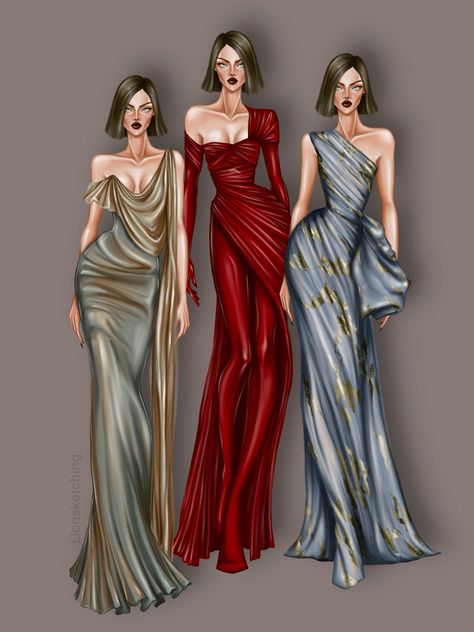
- Sketches and Illustrations:
- Include hand-drawn or digital fashion sketches that demonstrate your ability to translate ideas into garments. These sketches should cover a variety of silhouettes, styles, and concepts.
- Pay attention to proportion, anatomy, and details in your drawings. Each sketch should tell a story about the garment it represents.
- Technical Flats (Technical Drawings):
- These are precise, to-scale drawings that show the garment from different angles. Technical flats are essential for demonstrating your understanding of garment construction and technical skills.
- Include both front and back views, and detail features like seams, darts, pleats, and fastenings.
- Fabric Swatches and Textures:
- Attaching fabric swatches or texture samples adds a tactile element to a physical portfolio and gives a better sense of the garment’s design.
- In digital portfolios, fabric choices can be represented through images and texture overlays to convey how the material would look and behave.
- Photos of Finished Garments or Collections:
- Showcase photographs of completed pieces from your collections. Professional, high-quality images are essential to effectively display the craftsmanship of your work.
- Include multiple angles of the garments, such as full-length shots, close-ups of details, and images of the garments being worn or styled.
- If available, include images from fashion shows, editorials, or lookbooks that feature your work.
- Concept Development and Process:
- This section highlights your design process, from concept to creation. Include rough sketches, fabric exploration, and images of the garment in progress.
- Show how your ideas evolved and the creative decisions made along the way. This offers insight into your ability to work through design challenges and refine your vision.
- Specialty Work (Optional):
- If you have a specific area of expertise, such as draping, embroidery, textile design, or sustainable fashion, include samples of this work. Demonstrating a niche skill can set you apart from other designers.
- Additionally, if you design accessories, footwear, or jewelry, you should showcase those pieces as well.
- Digital Media (Optional):
- For digital portfolios, you may include short videos, 3D renderings, or animations that show your designs in motion. Virtual fashion shows or video presentations of garments offer a modern, dynamic element to your portfolio.
- Collections:
- If you have designed full collections, include them in the portfolio. Make sure each collection has a clear theme and showcases a cohesive narrative, color palette, and aesthetic.
- Highlight 4–6 key looks from each collection and explain the inspiration behind it.

How to Structure a Fashion Portfolio:
- Start Strong:
- Your first few pages should grab attention and immediately showcase your strengths. Begin with your most impactful pieces to create a lasting first impression.
- Tell a Story:
- Arrange your portfolio in a way that tells a cohesive story. You can organize it by themes, seasons, or collections. The flow of the portfolio should be logical and easy to follow.
- Balance Visuals and Text:
- While visuals are the focus, short written descriptions are important to explain your thought process, inspiration, and design decisions. Keep text concise and relevant to avoid overwhelming the viewer.
- Show Versatility:
- Include a variety of work that shows your ability to design across different categories (e.g., casualwear, eveningwear, streetwear) or design techniques (e.g., draping, tailoring, pattern-making).
- Customization:
- Tailor your portfolio to the specific job or school you’re applying to. For instance, if you’re applying for a menswear position, focus on showing your menswear designs. Customizing the portfolio shows that you’ve researched the company and understand their needs.
Tips for Presenting Your Fashion Portfolio:
- Quality Over Quantity: Focus on showcasing your best work rather than including every design you’ve ever created. A well-curated portfolio is more impressive than a large, unfocused collection of work.
- Keep It Updated: Continuously update your portfolio with new projects and collections to reflect your current skills and design aesthetic. Outdated work might not represent your abilities as a designer today.
- Professional Presentation: For physical portfolios, use high-quality printing and professional binding. For digital portfolios, ensure the website or PDF is easy to navigate and free of technical issues.
- Seek Feedback: Before presenting your portfolio, seek feedback from mentors, peers, or professionals in the fashion industry. They can offer valuable insights on how to improve the flow and impact of your portfolio.
The Importance of a Fashion Portfolio in Building a Career:
- Gateway to Opportunities: Whether you are applying for a design school, internship, or job, your portfolio is often the deciding factor. It serves as your proof of skill and creativity.
- A Tool for Networking: A portfolio can be shared with industry professionals during networking events or fashion shows. Having a well-crafted portfolio ready can open doors to new opportunities.
- Reflects Professionalism: A well-organized, polished portfolio shows that you take your work seriously and are committed to your craft. It speaks to your level of professionalism and attention to detail.
Conclusion:
A fashion portfolio is a vital tool for any fashion designer looking to break into the industry or advance their career. It showcases not only your creative abilities but also your technical expertise and vision as a designer. Crafting a thoughtful, well-organized portfolio that highlights your strengths and individuality is key to making a lasting impression in the competitive world of fashion design.
