How to Make WordPress Website ?
Step 1: Get a Domain Name and Hosting
- Domain Name: Choose a domain name that represents your brand or business. Use domain registration services like GoDaddy, Namecheap, or Google Domains to purchase your domain.
- Hosting: Select a hosting provider that meets your website’s needs. Popular options include Bluehost, SiteGround, and HostGator. Purchase a hosting plan that suits your budget and requirements.

Step 2: Install WordPress
Most hosting providers offer easy ways to install WordPress. Here’s a general guide:
- Log in to your hosting account.
- Navigate to your control panel.
- Look for the WordPress icon (often found under “Website” or “Softaculous Apps Installer”).
- Click on the icon and follow the instructions to install WordPress. You’ll need to choose your domain and fill in some basic details.
Step 3: Choose a Theme
- Access the WordPress Dashboard: Log in to your WordPress admin panel (usually at yourdomain.com/wp-admin) using the credentials provided during installation.
- Navigate to Appearance > Themes: Here, you can browse through thousands of free and premium themes. Click on “Add New” to search for themes based on your preferences.
- Install and Activate a Theme: Once you’ve found a theme you like, click “Install” and then “Activate” to make it your site’s design.
Step 4: Customize Your Website
- Access the Customizer: In the WordPress Dashboard, go to Appearance > Customize. Here, you can customize various aspects of your site, including colors, fonts, header, and footer.
- Add Your Content: Click on “Pages” in the WordPress Dashboard to add new pages for your website. You can also create a blog section by adding posts.
Step 5: Install Essential Plugins

- Access the Plugins Section: In the WordPress Dashboard, go to Plugins > Add New.
- Search for Essential Plugins: Some essential plugins include Yoast SEO (for SEO optimization), WPForms (for creating contact forms), and UpdraftPlus (for backup).
- Install and Activate Plugins: Click on “Install” and then “Activate” for each plugin you want to use.
Step 6: Set Up Your Site’s Navigation
- Create a Menu: In the WordPress Dashboard, go to Appearance > Menus. Create a new menu and add your pages to it.
- Assign the Menu: After creating your menu, assign it to a location (such as the primary menu) where you want it to appear on your site.
Step 7: Optimize Your Website for SEO
- Install Yoast SEO Plugin: If you haven’t already, install and activate the Yoast SEO plugin.
- Optimize Your Pages and Posts: Yoast SEO provides guidance on optimizing your content for search engines. Follow their recommendations to improve your site’s SEO.
Step 8: Launch Your Website
- Preview Your Site: Before launching, preview your site to ensure everything looks and functions as intended.
- Launch Your Website: Once you’re satisfied with the look and functionality of your site, it’s time to launch it! Share it with the world and start promoting your brand or business.
Creating a WordPress website is an exciting journey that allows you to showcase your brand or business online. By following these steps, you can create a professional-looking website that effectively represents your brand and engages your audience.
What is Domain Name ?
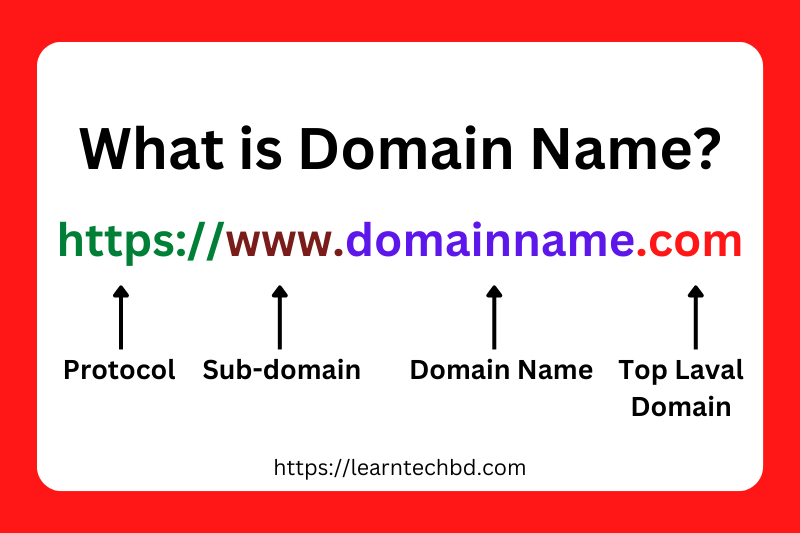
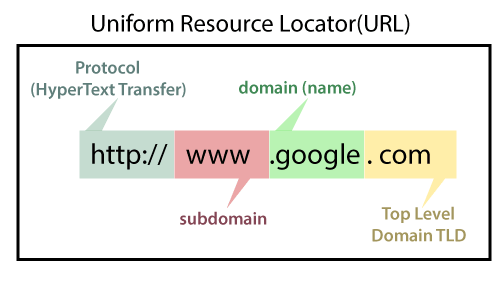
- Internet Domain: In the context of the internet, a domain refers to a unique and human-readable address used to identify a specific location or resource on the World Wide Web. For example, “www.example.com” is a domain name. It is part of the URL (Uniform Resource Locator) and is used to access websites and other resources on the internet.
- Mathematics: In mathematics, a domain can refer to the set of possible input values for a function. It is the set of all possible values that you can plug into a function to get a valid output. For example, in the function f(x) = x^2, the domain is all real numbers because you can square any real number and get a valid result.
- Computer Science: In computer science, a domain can refer to a specific area or subject of expertise, such as a domain of knowledge or a domain of authority. It can also refer to a network of computers under the control of a single entity, often used in the context of domain controllers in a Windows network.
- Business: In business, a domain can refer to a specific industry or market sector. For example, the automotive industry is a domain within the broader business world.
- Legal: In legal contexts, a domain can refer to a sphere of knowledge or activity that is subject to specific rules, regulations, or laws. For instance, intellectual property law covers the domain of copyrights, patents, and trademarks.
- Biology: In biology, a domain is one of the highest levels of classification used to categorize organisms. There are three main domains of life: Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya, which include all living organisms on Earth.
- Psychology: In psychology, a domain can refer to a specific area of study or specialization, such as clinical psychology or developmental psychology.
The meaning of “domain” can vary widely depending on the context in which it is used, so it’s important to consider the specific domain when interpreting the term.
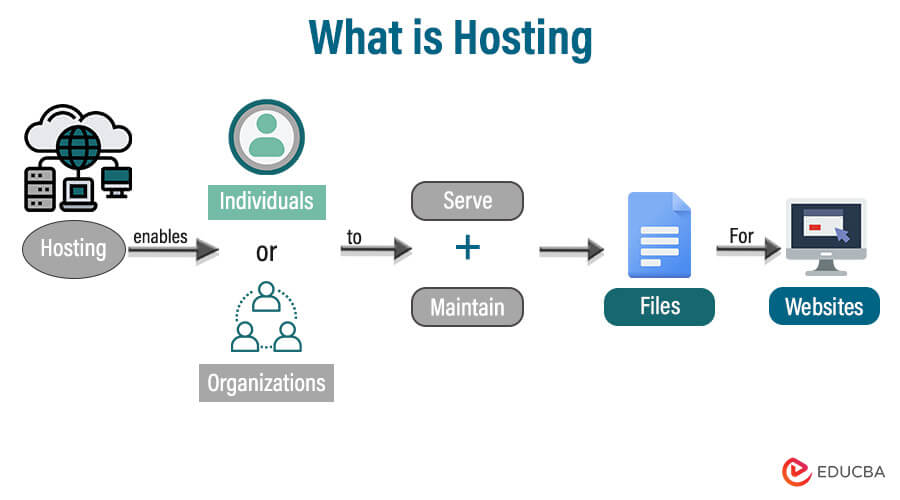
What is Hosting ?

- These servers are configured to handle web requests, serve web pages, and manage databases, among other tasks.
- Types of Hosting:
- Shared Hosting: In shared hosting, multiple websites share the same server resources (CPU, RAM, storage). It is a cost-effective option suitable for small to medium-sized websites with moderate traffic.
- Virtual Private Server (VPS) Hosting: VPS hosting involves partitioning a physical server into multiple virtual servers, each with its own dedicated resources. It offers more control and scalability compared to shared hosting.
- Dedicated Hosting: With dedicated hosting, an entire server is dedicated to a single website or client. This provides maximum control, performance, and customization but is more expensive.
- Cloud Hosting: Cloud hosting uses a network of virtual servers across multiple physical machines. It offers scalability, reliability, and flexibility, with clients paying for the resources they use.
- Managed WordPress Hosting: This is a specialized hosting service tailored for WordPress websites, including optimized performance, security, and WordPress-specific support.
- Domain and DNS: Hosting often includes domain registration or integration, allowing users to associate a web address (e.g., www.example.com) with the hosted content. Domain Name System (DNS) settings are configured to point to the hosting server’s IP address.
- Storage and Bandwidth: Hosting providers offer various storage and bandwidth plans. Storage refers to the amount of disk space available for files, databases, and content. Bandwidth determines the amount of data transfer allowed, which affects website traffic and file downloads/uploads.
- Security: Hosting services often include security features like firewalls, SSL certificates, and malware scanning to protect websites from cyber threats.
- Maintenance and Support: Hosting providers may offer maintenance services, software updates, and technical support to ensure the smooth operation of hosted websites.
- Uptime: Hosting providers strive for high uptime percentages (e.g., 99.9%) to minimize website downtime and ensure accessibility to users.
- Backup and Recovery: Hosting services may include regular backups of website data and the ability to restore content in case of data loss or issues.
Choosing the right hosting plan and provider depends on factors such as the type and size of your website, expected traffic, budget, technical expertise, and specific requirements. Different hosting options cater to different needs, so it’s essential to select the one that best suits your project or business.
Domain And Hosting Provide Company Name
- GoDaddy: One of the largest and most popular domain registrars in the world, known for its wide range of domain extensions and additional services.
- Namecheap: Offers affordable domain registration services and is known for its user-friendly interface and free WHOIS privacy protection.
- Google Domains: Google’s domain registration service, which provides a straightforward interface and integration with other Google services.
- Domain.com: Offers domain registration along with hosting and website building services.
Web Hosting Providers:
- Bluehost: A popular hosting provider, recommended by WordPress, offering shared hosting, VPS hosting, and dedicated servers.
- SiteGround: Known for its excellent customer support and WordPress hosting solutions.
- HostGator: Offers a wide range of hosting options, including shared hosting, VPS hosting, and dedicated servers.
- A2 Hosting: Known for its fast hosting services and developer-friendly features.
- InMotion Hosting: Offers a variety of hosting options with a focus on business hosting.
- DreamHost: Known for its robust hosting services and commitment to open-source software.
- WP Engine: Specializes in managed WordPress hosting with a strong focus on speed and security.
- Liquid Web: Provides managed hosting solutions for businesses, including dedicated servers and cloud hosting.
- Hostinger: Offers affordable hosting solutions with a strong global presence.
- iPage: Known for its budget-friendly hosting plans and website builder.
Remember that the best domain and hosting provider for you will depend on your specific needs, budget, technical expertise, and the type of website or project you are planning. It’s a good practice to research and compare providers to find the one that aligns with your requirements.
