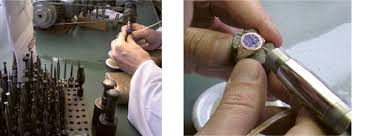
Auto Blocker – Diamond Processing
SECTOR: GEMS & JEWELLERY
SUB-SECTOR: Diamond processing
OCCUPATION: Blocking
REFERENCE ID: G&J/Q4602
ALIGNED TO: NCO-2015
Brief Job Description : Individuals work with the auto-blocking machine and
make the basic four (or eight) bottom and top facets of a diamond in order to
make it ready for final polishing or brilliance. For auto blocking, the stone is set
in a dop. Then dop is fixed in the auto-blocking machine and held down on a
revolving cast-iron scaife charged with diamond dust. Also known as Blocking
Operator or Operator, the auto blocker uses auto-blocking machine to create
the base four or eight bottom and top facets.
Personal Attributes: The job requires the individual to have: attention to
details; good eyesight; steady hands; ability to work in a process driven team;
ability to work for long hours in standing position; ability to multitask; and a lot
of patience.
Keywords /Terms Description
Sector Sector is a conglomeration of different business operations having similar
business and interests. It may also be defined as a distinct subset of the
economy whose components share similar characteristics and interests.
Sub-sector Sub-sector is derived from a further breakdown based on the characteristics
and interests of its components.
Occupation Occupation is a set of job roles, which perform similar/ related set of functions
in an industry.
Job role Job role defines a unique set of functions that together form a unique
employment opportunity in an organisation.
Occupational Standards
(OS)
OS specify the standards of performance an individual must achieve when
carrying out a function in the workplace, together with the knowledge and
understanding they need to meet that standard consistently. Occupational
Standards are applicable both in the Indian and global contexts.
Performance Criteria Performance criteria are statements that together specify the standard of
performance required when carrying out a task.
National Occupational
Standards (OS)
NOS are occupational standards which apply uniquely in the Indian context.
Qualifications Pack (QP) QP comprises the set of OS, together with the educational, training and other
criteria required to perform a job role. A QP is assigned a unique qualifications
pack code.
Unit Code Unit code is a unique identifier for an Occupational Standard, which is denoted
by an ‘N’
Unit Title Unit title gives a clear overall statement about what the incumbent should be
able to do.
Description Description gives a short summary of the unit content. This would be helpful to
anyone searching on a database to verify that this is the appropriate OS they
are looking for.
Scope Scope is a set of statements specifying the range of variables that an individual
may have to deal with in carrying out the function which have a critical impact
on quality of performance required.
Knowledge and
Understanding
Knowledge and understanding are statements which together specify the
technical, generic, professional and organisational specific knowledge that an
individual needs in order to perform to the required standard.
Organisational Context Organisational context includes the way the organisation is structured and how
it operates, including the extent of operative knowledge managers have of their
relevant areas of responsibility.
Technical Knowledge Technical knowledge is the specific knowledge needed to accomplish specific
designated responsibilities.
Core Skills/ Generic
Skills
Core skills or generic skills are a group of skills that are the key to learning and
working in today’s world. These skills are typically needed in any work
environment. In the context of the OS, these include communication related
skills that are applicable to most job roles.
Keywords /Terms Description
NOS National Occupational Standard(s)
NSQF National Skills Qualifications Framework
QP Qualifications Pack
Unit Code G&J/N4601
Unit Title
(Task) Dop the diamond for blocking
Description This OS unit is about fixing bruted diamond in the pot with accurate alignment
Scope This unit/task covers the following:
Setting rough diamond in the pot
Maintaining productivity
Controlling defects
Performance Criteria(PC) w.r.t. the Scope
Element Performance Criteria
Setting rough
diamond in the pot
To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to:
PC1. ensure accurate fixing of diamond as per the blocking required
PC2. ensure accurate alignment and levelling of the diamond on the dop
Maintaining
productivity
PC3. achieve the productivity in terms of carats or number of pieces as set by the
company
PC4. ensure timely delivery for further processing
Controlling defects PC5. ensure no damage to the diamond during fixing process
PC6. ensure no breakage while placing the cover in the press
A. Organizational
Context
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand:
KA1. Company’s policies on: quality and delivery standards, safety and hazards,
integrity and personnel management
KA2. Non–disclosure of “confidential information” provided by the company either
orally or in writing marked as confidential
KA3. Liability arising out of loss, theft, or inadvertent disclosure of confidential
information
KA4. Work flow involved in company’s product development process
KA5. Importance of the individual’s role in the workflow
KA6. Reporting structure
KA7. Issue return procedures followed by the company
B. Technical
Knowledge
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand:
KB1. Shape, cut, clarity, carat, and physical characteristics of the diamond
KB2. To match the specifications of the diamonds such as shape, size and quantity,
as per those mentioned on the packet issued
KB3. Select the pot as per the size, shape of the diamond and type of blocking
required (table pots for table cutting, top pots for top blocking and bottom
pots for bottom blocking, pots for manual or auto blocking)
KB4. Techniques of fixing of diamonds on pot without breakage
KB5. Fix the cover on the bottom pot using a manual press
KB6. Ensure there is no breakage while using the press
KB7. Use sticking agents like lac, white cement, etc. (if required) as prescribed
KB8. Use of an eye glass in order to check alignment
KB9. Potential work hazards
Skills (S) [Optional]
A. Core Skills/
Generic Skills
Writing Skills
The user/ individual on the job needs to know and understand how to:
SA1. Fill the requisition slip for tools and consumables
SA2. Document work done for status and performance appraisal
Reading Skills
SA3. To read descriptions on the diamond packets/ bags
Oral Communication (Listening and Speaking skills)
SA4. To discuss task, schedules, and work-loads with co-workers and supervisors
SA5. To understand instructions and report problems
SA6. To share work load as required
SA7. To assist others who require help
B. Professional Skills Decision Making
The user/ individual on the job needs to know and understand how to:
SB1. Make decisions pertaining to be the selection for particular type of blocking
Plan and Organize
SB2. Plan and organize maintenance of tools and machines used
SB3. Plan and organize the tools and consumables on the work bench for efficient
work management
Customer Centricity
N.A.
Problem Solving
SB4. Minimize damage or loss of any diamond during the doping process
SB5. To assess the quality of the pot / cover being used
SB6. To identify immediate or temporary solutions to avoid delays
Analytical Thinking
SB7. To plan the work to improve productivity and quality of setting
Critical Thinking
SB8. To spot process disruptions and delays
Unit Code G&J/N4605
Unit Title
(Task) Operate auto-blocking machine to create facets on diamond
Description This OS unit is about using the auto blocking machine for creating basic four/eight
bottom and top facets on a diamond as per the planned dimensions or the objective
fixed by the company, to give a basic shape to the diamond before it goes for final
polishing or brillianting
Scope This unit/task covers the following:
Operating the blocking machine
Achieving quality of blocking
Achieving productivity
Controlling defects
Multitasking
Element Performance Criteria
Operating the
blocking machine
To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to:
PC1. ensure accurate parameters are entered of dimensions of diamond in the
machine
PC2. operate and maintain the machine
Achieving quality of
blocking
PC3. achieve accurate proportion and symmetry of the facets as per design
requirement
PC4. remove all the inclusions while blocking as per plan
PC5. ensure accurate bagging and labelling of the diamonds before returning
Achieving
productivity
PC6. achieve the productivity in terms of carats or number of pieces as set by the
company
PC7. achieve timely delivery for further processing
Controlling defects PC8. ensure no flaws due to faulty polishing such as extra facets, natural surface,
nicks, scratches, polish lines, burning marks, abrasions
PC9. ensure no breakage of culet point
PC10. minimize damage, weight loss and breakage
PC11. repair a damaged stone
Multitasking PC12. work on different types of blocking machines and technologies
Knowledge and Understanding (K)
A. Organizational
Context
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand:
KA1. Company’s policies on: quality and delivery standards, safety and hazards,
integrity and personnel management
KA2. Non–disclosure of “confidential information” provided by the company either
orally or in writing marked as confidential
KA3. Liability arising out of loss, theft, or inadvertent disclosure of confidential
information
KA4. Work flow involved in company’s product development process
KA5. Importance of the individual’s role in the workflow
KA6. Reporting structure
KA7. Issue return procedures followed by the company
KA8. Typical customer profile and market trends
KA9. Specialization area of the company (size, clarity, shape, quality, etc. of
diamonds)
KA10. Diamond processing objective of the company, e.g. maximizing yield,
maximizing clarity, etc.
B. Technical
Knowledge
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand:
KB1. Blocking procedure of diamonds
KB2. Computer and blocking machine operations
KB3. Bruting and coning
KB4. Polishing process
KB5. 4Cs of diamond (Colour, Cut, Clarity and Carat)
KB6. Use of various scopes in diamond processing
KB7. Using proportion and symmetry analyzer machine
KB8. Geometry to understand the angles and symmetry
KB9. Process of preparation of scaife
KB10. Repair work
KB11. Valuation of diamonds depending on different dimensions
KB12. Uses of different types of tools and materials for different purposes and end
results
KB13. Maintenance and preparation of the tools as per job requirement
KB14. Potential work hazards, particularly, when using machine tools
. Core Skills/
Generic Skills
Writing Skills
The user/ individual on the job needs to know and understand how to:
SA1. To document work done for status and performance appraisal
SA2. To report diamond losses via documentation as per company policy
Reading Skills
SA3. To read descriptions on the job packets/ bags
SA4. To enter data on blocking machine and read its progress
SA5. To read the dimensions specified by the proportion analyser machine
Oral Communication (Listening and Speaking skills)
SA6. Discuss task lists, schedules, and work-loads with co-workers
SA7. To understand instructions and report problems
SA8. To share work load as required
SA9. To assist others who require help
SA10. To share knowledge with co-workers
SA11. To operate multiple machines
B. Professional Skills Decision Making
The user/ individual on the job needs to know and understand how to:
SB1. Make decisions pertaining to facet in order to yield maximum value for the
finished diamond, where no design is provided
Plan and Organize
SB2. To plan work for maximum productivity
SB3. To plan the best cut to get maximum value from the diamond
SB4. Plan and organize the schedule for maintenance of tools and machines
Customer Centricity
N.A.
Problem Solving
SB5. To rectify defects occurred
SB6. Refer technical problems with any part of machine to supervisor
SB7. Refer damage while blocking to supervisor
Analytical Thinking
SB8. To minimise weight loss
Critical Thinking
SB9. To spot process disruptions and delays
Unit Code G&J/N9901
Unit Title
(Task) Coordinate with others
Description This OS unit is about communicating with colleagues, seniors and outside parties in
order to achieve the deliverables on schedule
Scope This unit/task covers the following:
Interacting with supervisor
Interacting with colleagues within and outside the department
Interacting with outside parties
Performance Criteria(PC) w.r.t. the Scope
Element Performance Criteria
Interacting with
supervisor
To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to:
PC1. coordinate for receiving work instructions and raw materials from reporting
supervisor
PC2. communicate to the reporting supervisor about process flow improvements,
product defects received from previous process, repairs and maintenance of
tools and machinery as required
PC3. communicate to reporting supervisor about operation details and hazards
PC4. interact with supervisor regarding compliance of company policy and rules
Interacting with
colleagues within and
outside the
department
PC5. coordinate with colleagues to share work, as per the workload
PC6. communicate and discuss work flow related difficulties in order to find
solutions with mutual agreement
PC7. coordinate and receive feedback from quality control department
PC8. coordinate for putting team goals over individual goals
PC9. resolve conflicts by communicating with colleagues and other departments
PC10. coordinate with colleagues regarding multitasking in other departments with
requirements
Interacting with
outside parties
PC11. adhere to nondisclosure policy of the company in all outside coordination
Knowledge and Understanding (K)
A. Organizational
Context
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand:
KA1. Company’s policies on: preferred language of communication, reporting and
escalation policy, quality delivery standards, and personnel management
KA2. Company’s policies on non-disclosure of “confidential information” provided
by the company either orally or in writing marked as confidential
KA3. Liability arising out of loss, theft, or inadvertent disclosure of confidential
information
KA4. Reporting structure
B. Technical
Knowledge
The user/ individual on the job needs to know and understand how to:
KB1. Various categories of people that one is required to communicate and
coordinate within the organization
KB2. Importance of effective communication in the workplace
KB3. Importance of teamwork in organization and individual success
KB4. Various components of effective communication
KB5. Key elements of active listening
KB6. Barriers to effective communication
KB7. Importance of avoiding casual expletives and unpleasant terms while
communicating professional circles
KB8. Common reasons for interpersonal conflict
KB9. Expressing and addressing grievances appropriately and effectively
KB10. What constitutes disciplined behavior for a working professional
A. Core Skills/
Generic Skills
Writing Skills
The user/ individual on the job needs to know and understand how to:
SA1. Write instructions, remarks, job sheets, basic information, technical details
etc. in preferred local language of communication and English
Reading Skills
SA2. Read preferred language of communication as prescribed by the company
SA3. Read job sheets and interpret technical details mentioned in the job sheet
Oral Communication (Listening and Speaking skills)
SA4. Discuss task lists, schedules, and work-loads with co-workers
SA5. Be a good listener
SA6. Be effective in communicating the issues faced to the supervisor
SA7. Avoid using jargon, slang or acronyms when communicating
B. Professional Skills Decision Making
The user/ individual on the job needs to know and understand how to:
SB1. Spot and communicate potential areas of disruptions to work process and
report the same
SB2. Report to supervisor and or to deal with a colleague individually, depending
on the type of concern
Plan and Organize
SB3. Collate information and communicate in a manner that is clear and
comprehensive to colleagues and supervisor
SB4. Convey accurate information to all internal as well as external customers (or
right information to right person)
Problem Solving
SB5. How to handle critical situations caused due to communication issues at
workplace and solve problems without blaming others
Analytical Thinking
SB6. Analyse the work processes by interacting with others and adopting best
practices
SB7. Use prior experience to observe and reflect for development of ideas
Critical Thinking
SB8. Think through the problem, evaluate the possible solution(s) and suggest an
optimum /best possible solution(s)
SB9. Deal with clients lacking the technical background to solve the problem on
their own
SB10. Spot process disruptions and delays and report and communicate with
solutions
SB11. Identify immediate or temporary solutions to resolve delays
SB12. Apply, analyze, and evaluate the information gathered from observation,
experience, reasoning, or communication, as a guide to thought and action
Unit Code G&J/N9902
Unit Title
(Task) Maintain health and safety at workplace
Description This OS unit is about being aware of, communicating and taking steps towards
minimizing potential hazards and dangers of accidents on the job and maintaining
health and safety
Scope This unit/task covers the following:
Health and safety in work area
Fire safety
Emergencies, rescue and first aid procedures
Performance Criteria(PC) w.r.t. the Scope
Element Performance Criteria
Health and safety in
work area
To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to:
PC1. identify and use appropriate protective clothing/equipment for specific tasks
and work
PC2. identify hazardous job activities in his/her job and communicate the possible
causes of risks or accidents in the workplace
PC3. carry out safe working practices while dealing with hazards to ensure safety
of self and others
PC4. identify and avoid doing any tasks or activities in a bad working position
PC5. practice appropriate working postures to minimise occupational health
related issues
Fire safety PC6. use the appropriate fire extinguishers on different types of fire
PC7. demonstrate rescue techniques applied during fire hazard
PC8. demonstrate good housekeeping in order to prevent fire hazards
PC9. demonstrate the correct use of any fire extinguisher
Emergencies, rescue
and first aid
procedures
PC10. administer appropriate first aid procedure to victims wherever required eg.in
case of bleeding, burns, choking, electric shock etc.
PC11. respond promptly and appropriately to an accident situation or medical
emergency
PC12. participate in emergency procedures such as raising alarm, safe evacuation,
correct means of escape, correct assembly point etc.
Knowledge and Understanding (K)
A. Organizational
Context
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand:
KA1. Company’s policies on: safety and hazards and personnel management
KA2. Names and location of documents that refer to health and safety in work
place
KA3. Reporting structure
B. Technical
Knowledge
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand:
KB1. Meaning of “hazards” and risks
KB2. Health and safety hazards commonly present in the work place and related
precautions
KB3. Various dangers associate with use of electrical equipment
KB4. Preventative and remedial actions to be taken in case of exposure to toxic
material
KB5. Methods of accident prevention
KB6. How different chemicals react and what could be the danger from them
KB7. How to use machines and tools without causing any harm to the body
KB8. Importance of using protective clothing/ equipment while working
KB9. Precautionary activities to prevent the fire accident
KB10. Various causes of fire
KB11. Techniques of using different fire extinguishers
KB12. Different material s materials used for extinguishing fire
KB13. Rescue techniques applied during a fire hazard
KB14. Various types of safety signs and what they mean
KB15. Appropriate basic first aid treatment relevant to condition e.g. bleeding minor
burns eye injuries
KB16. Potential impact to a person who is moved incorrectly
A. Core Skills/
Generic Skills
Writing Skills
The individual on the job needs to know and understand how to:
N.A.
Reading Skills
SA1. Read and comprehend basic content to read labels, charts, signage’s
SA2. Read and comprehend basic English to read manuals of operations
Oral Communication (Listening and Speaking skills)
SA3. Effectively communicate the risk of not following safety measures
B. Professional Skills Decision Making
The individual on the job needs to know and understand how to:
SB1. Report potential sources of danger
SB2. Follow the relevant prescribed procedure in the event of an accident
SB3. Wear appropriate safety gear to avoid an accident
Plan and Organize
SB4. Learn from past mistakes regarding use of hazardous machines or chemicals
Customer Centricity
N. A.
Problem Solving
SB5. Adhere to and guide others to follow prescribed procedures related to health
and safety
Analytical Thinking
SB6. Analyse untoward incidents from the past and implement correct use of
machines, tools or hazardous chemicals
Critical Thinking
SB7. Critically analyse the processes carried out by self and by colleagues in the
department to spot potential hazards and safety issues
Criteria For Assessment Of Trainees
Job Role Auto Blocker – Diamond Processing
Qualification Pack G&J/Q4602
Sector Skill Council Gem & Jewellery
Guidelines for Assessment
- Criteria for assessment for each Qualification Pack will be created by the Sector Skill Council. Each Performance
Criteria (PC) will be assigned marks proportional to its importance in NOS. SSC will also lay down proportion of
marks for Theory and Skills Practical for each PC. - The assessment for the theory part will be based on knowledge bank of questions created by the SSC.
- Assessment will be conducted for all compulsory NOS, and where applicable, on the selected elective/option
NOS/set of NOS. - Individual assessment agencies will create unique question papers for theory part for each candidate at each
examination/training center (as per assessment criteria below). - Individual assessment agencies will create unique evaluations for skill practical for every student at each
examination/training center based on this criterion. - To pass the Qualification Pack, every trainee should score a minimum of 50% of aggregate marks to successfully
clear the assessment. - In case of unsuccessful completion, the trainee may seek reassessment on the Qualification Pack.