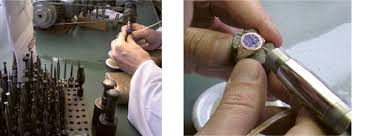
Kundan-Jadau Goldsmith
SECTOR: GEMS & JEWELLERY
SUB-SECTOR: Handmade gold and gems-set jewellery
OCCUPATION: Gold smithy (Specialised)
REFERENCE ID: G&J/Q0901
ALIGNED TO: NCO-2004/ 7313.30
Kundan-Jadau Goldsmith: Also known as ‘Kundan Goldsmith’, the Kundan-Jadau
Goldsmith makes specialised gold jewellery using, gold alloy, 24 karat gold, silver
and gemstones set in closed setting or Jadau style.
Brief Job Description: The individual at work works with hand and machine tools
to create specialised jewellery of gold using wax, pure silver and gold foil, enamel
paint, gemstones and flat diamonds. It is a highly creative job role.
Personal Attributes: The job requires the individual to have: aptitude for design;
attention to details; good eyesight; steady hands; ability to work for long hours in
sitting position; and a lot of patience. The individual must also be able to use
reflective skills in order to develop improved designs and work processes, and
analytical skills to avoid errors and hazards.
Unit Code G&J/N0904
Unit Title
(Task) Make components, frame, Kundan (24K gold) foil and Silver foil
Description This OS unit is about making Kundan jewellery along with enamelling and Jadau
(closed) setting using components and gemstones
Scope This unit/task covers the following:
Order precious metal or alloy for making components
Draw wire, strip or sheet
Make Kundan (24K gold) foil or Silver foil
Anneal the wire or strip or sheet for malleability while drawing or rolling
Make components
Make the frame
File the frame components for finishing
Control precious metal loss
Detect product defects and return completed wire to supervisor
Report problems in time
Performance Criteria(PC) w.r.t. the Scope
Element Performance Criteria
Preparing for making
Kundan-Jadau
jewellery
To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to:
PC1. understand specifications in terms of required components, e.g., wires or
chains, sheets, balls, collets
PC2. understand dimensions required such as thickness of wire, size and shape of
ball, and depth and shape of collet
PC3. assess quantity of precious metal or alloy required for making the components
PC4. roll metal bars/ingots to the appropriate thickness using wire drawing or rolling
machine
PC5. sharpen one end of the metal bar / rolled wire to ease the insertion of metal
bar / rolled wire into draw-plate cavity / hole
PC6. push the metal through the draw-plate and then draw it out using force, so as
to thin the wire step by step
PC7. repeat the process through consecutive small holes to get the required
thickness of wire
PC8. pass metal through roller machine or mill to make into strips or sheet of
appropriate thickness
Making Kundan To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to:
PC9. roll 24 karat gold metal into thin leaf by repeatedly using rolling machine and
hammering
PC10. roll silver metal into thin leaf using rolling machine
PC11. heat treat / anneal the sheets / wire and pickle it (pickling is boiling in
approximately 10% sulphuric acid solution, awareness of hazard notes is must),
after pickling, rinse it in plain or mild alkaline water
PC12. make rolls of thin leaf of gold and silver
PC13. assess whether the wire or strip type (e.g., spring) requires annealing
PC14. treat the wire or strip with heat using gas torch or furnace
PC15. set temperature according to the thickness of the wire or strip
PC16. remove the wire or strip from heat and quench in water to cool immediately
PC17. repeat the heating and cooling process after every drawing or rolling
To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to:
PC18. solder the ends to shape as a ring
PC19. connect pieces of wire together to make the chain as per design using the
weaving or soldering method as specified
PC20. to make ball, cut the sheet or strip as per the diameter of the ball
PC21. create two hemispheres of the ball and lock and join them by heating
PC22. or use hollow ball making machine to make gold balls from sheets
PC23. or fire small wire pieces on glass cotton to make small sized balls
PC24. connect the ends of sheet to make collet, give shape as per design and solder
PC25. check symmetry of design
PC26. lay the components and frame pieces on wax or lac and set in Plaster of Paris
(PoP) mixture or customised jigs
PC27. solder components to link to form frame as per design on both sides
PC28. remove PoP, level and strengthen joints in wax or lac
PC29. send completed frame for cleaning with brush and water or chemical solution
PC30. make components of required dimensions such as size and thickness
PC31. make components of required finish and evenness
PC32. draw or roll metal without overdrawing or splitting or cracking
PC33. anneal the wire, strips and sheets for required malleability for the thickness
required
PC34. limit precious-metal loss of damaged metal rod or wire
PC35. cut any sharp edges as per design
PC36. file for smooth finish of joined periphery as per the design requirement
PC37. file or grind outer surface for smoothness and required finish
PC38. file for correct dimensions, e.g., length, bend, flexibility, colour, evenness, size
and embellishments to be fitted
PC39. accurately link the ends to form even rings, collets or chains of required
dimensions
PC40. link, solder and file the components into frame of required finish and utility
PC41. achieve required flexibility, utility and symmetry of frame as per design
PC42. meet productivity target
PC43. complete work with minimum hazards and accidents
Controlling precious
metal loss and
checking quality
To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to:
PC44. collect precious metal dust or fragments dispersed during the day
PC45. tally account as per allowed standards for wire making
PC46. conduct regular cleaning for collection of gold as per company policy
PC47. identify the type of defect, e.g., damaged beyond repair
PC48. handover defective components to supervisor for melting or use elsewhere
PC49. rework on any quality check feedback and return
PC50. ensure timely delivery
Reporting problems To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to:
PC51. report equipment/machine failure
PC52. inform about tools shortage and their maintenance related issues
PC53. report reasons for anticipated delays that may adversely affect delivery
PC54. report malfunction of annealing torch or furnace deliver complete frames in
time by reporting well in advance, any problems faced or anticipated
A. Organizational
Context
(Knowledge of the
company /
organization and
its processes)
The individual on the job needs to know and understand:
KA1. company’s policies on: Acceptable limits of precious metal loss per product
type; delivery timelines; safety and hazards; security; and personnel
management
KA2. work flow involved in company’s jewellery manufacturing process, i.e., from
one goldsmith to another
KA3. importance of the individual’s role in the workflow
KA4. reporting structure
B. Technical
Knowledge
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand:
KB1. uses of different types of tools used in wire drawing and rolling such as ruler,
draw plates, pliers, hammer, bench block, cup bur, cutter, roller machine
KB2. gold and silver foil packing
KB3. properties of gold and silver leafs
KB4. different types of wax or lac and their use
KB5. precious-metal or gold alloy properties such as strength and malleability
KB6. heat treatments and intensity effect with respect to different types of gold
alloys, e.g., 18K gold requires less annealing than 10K or springs need
different treatment than annealing
KB7. potential work hazards, particularly, when using hand and machine tools
Skills (S) [Optional]
A. Core Skills/
Generic Skills
Basic reading and writing skills
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how:
SA1. to read notes and put notes on design
Measuring skills
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how:
SA2. to assess the material requirement for making wires of specified length and
thickness
SA3. to use gauge check the thickness of wire
SA4. to check symmetry of component made
B. Professional Skills Using tools and machines
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how:
SB1. to use roller machine for drawing wire or strip
SB2. to use tools for drawing wire such as: Gas torch or furnace for annealing wire
or strip; drawing tongs and draw plate for thinning diameter of wire and
required shape; wax or oil for lubrication
SB3. to use tools such as files and pliers
SB4. to use the right hole in draw plate and at correct angle for achieving the finish
as per design
SB5. to maintain tools and machines used
SB6. to use technology such as computer for visual aid and efficient working
Reducing precious metal loss
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand:
SB7. prescribed precious-metal loss for the entire jewellery piece
SB8. Precious-metal loss applicable for the component
SB9. how to reduce precious metal loss below the prescribed standards
SB10. how to collect broken or over rolled pieces, account in job sheet and return
SB11. how to follow company’s policies on collecting gold dust and fragments
SB12. how to suggest improvements in order to reduce precious metal loss limits
Reflective thinking
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to:
SB13. work in sitting or standing for long hours position with correct posture
SB14. maintain clean work environment and organise tools for ease of use
Critical thinking
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how:
SB15. to spot process disruptions and delays
SB16. to avoid hazards when using roller machine or draw plate or during annealing
Unit Code G&J/N0905
Unit Title
(Task) Engrave pattern and apply enamel paint
Description This OS unit is about applying enamel paint on the back and front sides of the
jewellery frame as per design
Scope This unit/ task covers the following:
Receive work from supervisor
Prepare gold jewellery surface for enamel paint application
Prepare the enamel
Apply enamel paint on gold jewellery surface
Fire, retouch and finish
Detect product defects
Check quality and return
Element Performance Criteria
Engraving and
enamel painting
To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to:
PC1. receive the design from supervisor and understand the enamelling
requirement, i.e., colour combinations, type of surface to be prepared, areas
for enamel painting, delivery schedule and methodology to use
PC2. order consumables such as enamel lumps, acids and chemicals, brush, handling
tools, safety gear and take stock of equipment such as kiln or furnace or oven
or gas torch
PC3. receive the jewellery to be enamelled
PC4. prepare jewellery surface for adhesion, uniform firing and even colour
distribution
PC5. stick gold sheet on hot wax; draw the design on wax using a pointed needle;
and engrave or scoop out metal from the sheet; remove wax
PC6. chisel the surface to be painted using chisel or graver for sparkling finish of
large base area or buff the surface for glossy finish or cut motifs
PC7. prepare enamelling area of even thickness in order to achieve even spread of
enamel while firing
PC8. prepare surface of optimum thickness for the enamel to hold an not chip or
crack at a later stage, taking care to protect the surface from being pierced or
punctured
PC9. apply enamel to a hollow surface after removing all moisture to avoid enamelsplitting at the time of firing because of moisture tapped in the hollow or
depressed area
PC10. remove from the surface any grease, oil grime and dust
PC11. clean or degrease using solvents or acid or cleaning solutions after preparing
the surface while avoiding any hand contact with the chemical used
PC12. crush the required quantities and colours of enamel lumps and grind with
mortar into fine powder using mortar and pestel (joy & ewly) and add
demineralised (DM) water to the lumps to avoid small particles, ground enamel
and debris from being dispersed in air
PC13. protect eyes and skin from injuries from dispersing debris which may contain
glass and other sharp dust particles; Use protective eyewear
PC14. repeatedly rinse fine powder and grind, adding Nitric acid to water in order to
remove impurities
PC15. take extreme care while rinsing the ground enamel using Nitric acid drops to
avoid skin burns or adverse acid reaction
PC16. transfer finely ground paste to a small dish or container with water at a level
slightly higher than the paste
PC17. check the paste solution for any impurities and water for any floating particles
PC18. add a few drops of vegetable glue as bonding agent for the paste
PC19. paint and apply colour on prepared surface using brushes with soft bristles
PC20. use jigs to hold the jewellery piece securely while painting
PC21. do not spill over paint during application on different sides of the jewel
PC22. apply separate colours in separate strokes, i.e., one after another and not all
together
PC23. ensure use of separate brushes and containers for different colours
PC24. leave the painted surface for a few minutes to dry
PC25. take care not to drop the jewellery piece after painting
PC26. place the painted jewellery piece in the kiln or oven or furnace using stainless
steel mesh for firing or use gas torch at recommended temperature for the
enamel
PC27. remove the jewellery from the kiln or oven or furnace or gas torch as soon as
the colour melts and flows
PC28. leave it to cool to room temperature
PC29. check the jewel for excess enamel and remove using Hydrofluoric acid
PC30. take extreme precaution while sing Hydrofluoric acid against inhalation, skin
burns or skin contact;
PC31. always keep soda-ash-water solution ready in the work area, to be used upon
contact with Hydrofluoric acid
PC32. re-fire the jewel for finish as per design, repeat if necessary
PC33. remove jewel from kiln, oven, furnace or gas torch and leave to cool
PC34. finish the surface with grinder and cutter to remove uneven enamel and gold
PC35. rinse with Hydrofluoric acid for uniform spread of enamel applied
PC36. re-fire for glossy finish
PC37. dry after every rinsing cycle and cool after each firing
PC38. use resin colours for non-traditional, i.e., non-Jaipuri or non-Bikaneri, style of
enamelling
PC39. achieve symmetry of design to be engraved or etched for applying enamel
PC40. achieve smooth finish of enamel paint as per design
PC41. ensure no overflow or excess enamel at the edges of the painted area
PC42. ensure that enamel prepared with no impurities
PC43. ensure no chipping or cracking enamel
PC44. prepare surface of thickness and evenness for long term enamel adhesion
PC45. fire at right temperature for the enamel to flow and set
PC46. achieve colour, vibrancy and gloss as per design
PC47. achieve hazard-free output after using acids and chemicals
Checking quality To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to:
PC48. inform supervisor if product has arrived with polishing, cleaning, filing or linking
defect from previous processes
PC49. understand the type of defect and send to relevant goldsmith
PC50. report impractical design
PC51. use needle to check for chipped or cracked enamel after final firing
PC52. in case it is chipped or cracked, leave the jewel in Hydrofluoric acid for 24-72
hour in order to remove the enamel completely and repeat the process
PC53. check weight and dimensions of jewellery as per design
PC54. return the completed enamelled jewel to supervisor or senior
PC55. deliver enamelled frame on time by reporting problems faced or anticipated
well in advanceA. Organizational Context (Knowledge of the company / organization and its processes) The individual on the job needs to know and understand: KA1. company’s policies on: Acceptable limits of gold loss per product type; delivery timelines; safety and hazards; security; and personnel management KA2. work flow involved in company’s jewellery manufacturing process, i.e., from one goldsmith to another KA3. importance of the individual’s role in the workflow KA4. reporting structure B. Technical Knowledge The individual on the job needs to know and understand: KB1. drawing designs and engraving KB2. jewellery making process and types of jewellery (product, styles, regional, traditional, making technique) KB3. types of enamel, such as transparent, opaque and opal or translucent and their properties: Transparent and opaque easier to apply than opal KB4. hard (firing at 750°C), medium (600-750°C) and soft (<650°C)enamels KB5. enamel available in lumps (longer shelf life), powder and paste forms KB6. choice of mortar and Prestel for grinding powder such as hardened steel, agate, stone that do not leave residue while grinding KB7. expansion and shrinkage rates of gold alloy used and that of the enamels used KB8. adverse effect of very thin base surface, poorly prepared surface or moisture on enamelling outcome KB9. adverse effect of dust and impurities in enamel or on base surface on the outcome KB10. recommended temperatures for different categories of enamel KB11. use of highly hazardous acids and chemicals such as Nitric acid or Hydrofluoric acids and safeguards KB12. filing and soldering
A. Core Skills/
Generic Skills
Basic reading and writing skills
The individual on the job needs to know and understand how:
SA1. to read notes and put notes on design
SA2. to read company policy documents
SA3. to read about enamelling and jewellery making techniques
Calculation and Geometry skills
The individual on the job needs to know and understand how:
SA4. to assess gold loss at each step of jewellery making so as to deliver product of
correct weight and size
SA5. to translate design into enamel painted jewellery
Teamwork and multitasking
The individual on the job needs to know and understand how:
SA6. to share work load with other setters as per capability and work load
SA7. to deliver the enamelled jewellery on time
B. Professional Skills Painting
The individual on the job needs to know and understand how:
SB1. to use creativity while painting layers of different colours of enamel
SB2. to enamel keeping in mind the requirements of finish, longevity of colour and
utility of the design
Using tools and consumables
The individual on the job needs to know and understand how:
SB3. to use demineralised water for grinding, washing and rinsing enamel
SB4. to use vegetable glue such as pomegranate seeds for bonding the enamel paste
SB5. to use Nitric acid to rinse ground enamel through drop bottles
SB6. to use Hydrofluoric acid to wash and remove excess enamel and achieve
smooth finish
SB7. to use polypropylene steel containers to handle acids
SB8. to use mortar and pestel to break and grind enamel lumps into fine powder
and grinding stones
SB9. to use porcelain and steel dishes for holding enamel paste during application
SB10. to use fine bristled brushes for painting
SB11. to use chisels and graves for preparing the base gold surface
SB12. to use temperature controlled kilns, ovens or furnaces for firing and steel wire
mesh for putting the jewel for firing
SB13. to use tongs, holders, spatula, plates, ceramic blocks and asbestos boards
SB14. to understand hazards involved with chemicals, furnaces and tools used
Reducing precious-metal loss
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand:
SB15. how to reduce precious metal loss below the prescribed standards
SB16. how to collect broken pieces, account in job sheet and return
SB17. how to follow company’s policies on collecting gold dust and fragments
SB18. how to suggest improvements in order to reduce precious metal loss limits
Reflective thinking
The individual on the job needs to know and understand how:
SB19. to improve work processes
SB20. use correct posture for performing the job without injuring body parts
SB21. to reduce gold loss and rework because of chipped or cracked enamel
Critical thinking
The individual on the job needs to know and understand how:
SB22. to spot process disruptions and delays
Unit Code G&J/N0803
Unit Title
(Task)
Set flat diamonds or gemstones using Jadau technique and string gemstones to
jewellery frame
Description This OS unit is about using the Jadau setting technique for setting gemstones, mainly,
flat diamonds (or polki diamonds) in the jewellery frame using silver foil and kundan
(24K gold) foil; it is also about stringing gemstones on to the jewellery frame
Scope This unit/task covers the following:
Receive sorted polki-diamonds or glass, gemstones and jewellery frame for
settingSet polki and other gemstone stones
String gemstones beads on along the lower periphery of the frame
File excess gold around gemstone setting
Detect product defects
Check quality and report problems
Performance Criteria(PC) w.r.t. the Scope
Element Performance Criteria
Jadau setting To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to:
PC1. understand different shapes, sizes and colour of stones
PC2. match stones in the bag with design
PC3. understand the closed setting requirement, i.e., with enamel on back side or
without
PC4. for polki-jadau setting, fill the empty collet on frame with molten wax
PC5. polish silver foil with Agate and apply on the back side of the polki stone with
hot wax; cut off excess foil from the side
PC6. place the polki-silver assembly on the hot wax and press with solder so that the
stone is set in place
PC7. use layers of 24K gold foil to press around the polki-silver assembly for secure
setting
PC8. for other gemstone setting, set the jewellery frame on lac or wax coated
wooden plate
PC9. set stones in the collet or channel or ring as per design
PC10. boil in hot water to remove lac and achieve clean surface
PC11. receive the bag of beads to be used for lining the jewellery
PC12. fit and secure the gemstone using the wire drawn and joined together
PC13. string the set gemstones using thin gold wire
PC14. link the assembled gemstone to the jewellery frame by soldering
PC15. understand design requirements such as correct length of jadau, prong, bend,
colour, evenness
PC16. file or cut sharp edges of prongs
PC17. grind for smooth surface
PC18. avoid over filing
PC19. achieve required shine for polki setting
PC20. achieve flawless setting as per design requirement
PC21. achieve even colour of stones set, i.e., no discolouration or breakage during
setting
PC22. set stones securely
PC23. stringing is even and secure
PC24. avoid damage to the rest of the frame during the process of setting
PC25. achieve productivity as per target
PC26. complete work with minimum hazards and accidents
Quality checking To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to:
PC27. inform supervisor if product has arrived with polishing, cleaning, filing or linking
defect from previous processes
PC28. understand the type of defect and send to relevant goldsmith
PC29. check visually in for any defects such as loose stone, tilted setting, marks, blank
spaces
PC30. check weight and dimensions of jewellery as per design
PC31. remove and re-set stone again if returned from QC
PC32. report tools shortage and their maintenance related issues
PC33. identify an report reasons for anticipated delays that may adversely affect
delivery
PC34. deliver stones set jewellery in time by reporting problems faced or anticipated
well in advance
A. Organizational
Context
(Knowledge of the
company /
organization and
its processes)
The individual on the job needs to know and understand:
KA1. company’s policies on: Acceptable limits of gold loss per product type;
delivery timelines; safety and hazards; security; and personnel management
KA2. work flow involved in company’s jewellery manufacturing process (from one
goldsmith to another)
KA3. importance of the individual’s role in the workflow
KA4. reporting structure
B. Technical
Knowledge
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand:
KB1. sorting similar shapes and size of stones as per design
KB2. 4Cs, i.e., colour, cut, clarity and carat
KB3. handmade jewellery making process
KB4. types of close set jewellery and jadau styles such as Jaipuri/ Bikaneri, Amritsari,
Delhi
KB5. uses of different types of tools and techniques for gemstone setting
KB6. different types of polki or flat diamonds and glass
KB7. different types of wax and their use in jewellery making
KB8. basic properties of gemstones and effect of reaction to pressure, heat and
chemicals
KB9. gold alloy properties for securing and rework, i.e., which alloy allows rework
KB10.filing and soldering
A. Core Skills/
Generic Skills
Basic reading and writing skills
The individual on the job needs to know and understand how:
SA1. to read notes and put notes on design
SA2. to use technology such as computer for visual aid or improving efficiency
Measuring and Geometry skills
The individual on the job needs to know and understand how:
SA3. to assess precious metal loss at each step of jewellery making so as to deliver
product of correct weight and size
SA4. to translate design into gems-set jewellery
SA5. to set the stone into collet at correct angle for secure and tilt-free placing
Teamwork and multitasking
The individual on the job needs to know and understand how:
SA6. to share work load with other setters as per capability and work load
SA7. to deliver frame to next work process on time
B. Professional Skills Reading design
The individual on the job needs to know and understand how:
SB1. to set stones as per design
SB2. to spot difficulties with respect to practicality of design
Using tools
The individual on the job needs to know and understand how:
SB3. to use the right hand tools for achieving secure setting as per design
SB4. to use tools so that they do not damage jewellery frame or gemstones
SB5. to use tools such as: hammer, tweezers, graver, scoop, wooden plates with lac,
gas torches, table light, needles, burrs, files and soldering system
SB6. to understand safety and hazards involved in using tools
Reducing precious metal loss
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand:
SB7. prescribed precious metal loss for the entire jewellery piece
SB8. precious-metal loss applicable for setting
SB9. how to reduce precious metal loss below the prescribed standards
SB10. how to follow company’s policies on collecting gold dust and fragments
SB11. how to account in job sheet and return
SB12. how to suggest improvements in order to reduce precious metal loss limits
Reflective thinking
The individual on the job needs to know and understand how:
SB13. to improve work processes
SB14. to work with good posture in a sitting position
SB15. maintain clean work environment and organise tools for ease of use
Critical thinking
The individual on the job needs to know and understand how:
SB16. to spot process disruptions and delays
Unit Code G&J/N9910
Unit Title
(Task) Respect IPR of company as well as competitors
Description This OS unit is about maintaining company’s IPR and avoiding infringement on
copyright of others
Scope This unit/task covers the following:
Protect company’s Intellectual Property Rights (IPR)
Avoid infringement to copyright of other companies
Performance Criteria(PC) w.r.t. the Scope
Element Performance Criteria
Respecting IPR To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to:
PC1. prevent leak of new designs to competitors by reporting on time
PC2. spot any infringement of company’s product or design patents
PC3. report IPR violations observed in the market, to supervisor or company heads
PC4. read copyright clause of the material published on the internet and any other
printed material
PC5. consult supervisor or senior management when in doubt about using publicly
available information
PC6. report any infringement observed in the company
PC7. spot plagiarism and report
PC8. understand rationale of patents and IPR
PC9. avoid being involved in IPR violations
Knowledge and Understanding (K)
A. Organizational
Context
The individual on the job needs to know and understand:
KA1. company’s policies on IPR, plagiarism and order leaks
KA2. company’s patented products
KA3. market trends and company’s unique product range
KA4. reporting structure
B. Technical
Knowledge
The individual on the job needs to know and understand:
KB1. basics of patents and IPR laws
KB2. how IPR protection is important for competitiveness of a company
Skills (S) [Optional]
A. Core Skills/
Generic Skills
Communication skills
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how:
SA1. to effectively communicate any observed IPR violations or design leaks
B. Professional Skills Decision making
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand when and how:
SB1. to report sources of IPR violations
Reflective thinking
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how:
SB2. to learn from past mistakes and report IPR violations on time
Critical thinking
The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how:
SB3. to spot signs of violations and alert authorities in time
Unit Code G&J/N9912
Unit Title
(Task) Interact with colleagues and seniors
Description This OS unit is about communicating with colleagues and seniors in order to maintain
smooth ad hazards free work flow
Scope This unit/task covers the following:
Interact with supervisor
Interact with colleagues within and outside the department
Performance Criteria(PC) w.r.t. the Scope
Element Performance Criteria
Interaction with
supervisor
To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to:
PC1. receive and understand work instructions from reporting superior
PC2. communicate to reporting supervisor about process flow improvements,
product defects received from previous process, repairs and maintenance of
tools and machinery as required
PC3. communicate any potential hazards or expected process disruptions
PC4. handover completed work to supervisor
PC5. understand the work output requirements
PC6. comply with company policy and rule
PC7. deliver quality work on time as required by reporting any anticipated reasons
for delays
Interactions with
colleagues and other
departments
To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to:
PC8. work as a team with colleagues and share work as per their or own work load
and skills
PC9. work with colleagues of other departments such as frame making or
component making or polishing or setting or stores
PC10. communicate an discuss work flow related difficulties in order to find solutions
with mutual agreement
PC11. receive feedback from QC and rework in order to complete work on time
PC12. put team over individual goals
PC13. resolve conflicts and multi-task
Knowledge and Understanding (K)
A. Organizational
Context
(Knowledge of the
company /
organization and
its processes)
The individual on the job needs to know and understand:
KA1. company’s policies on personnel management
KA2. work flow involved in company’s jewellery manufacturing process
KA3. importance of the individual’s role in the workflow
KA4. reporting structure
B. Technical
Knowledge
The individual on the job needs to know and understand:
KB1. how to communicate effectively
KB2. how to build team coordination
Skills (S) [Optional]
A. Core Skills/
Generic Skills
Teamwork and some multitasking
The individual on the job needs to know and understand how:
SA1. to share work load as required
SA2. to deliver product to next work process on time
B. Professional Skills Decision making
The individual on the job needs to know and understand:
SB1. how to report potential areas of disruptions to work process
SB2. when to report to supervisor and when to deal with a colleague depending on
the type of concern
Reflective thinking
The individual on the job needs to know and understand:
SB5. how to improve work process
Critical thinking
The individual on the job needs to know and understand:
SB6. how to spot process disruptions and delays
Unit Code G&J/N9914
Unit Title
(Task) Work towards having a safe work environment
Description This OS unit is about being aware of and communicating potential hazards and
dangers of accidents on the job
Scope This unit/task covers the following:
Understand potential sources of accidents
Communicate to reporting supervisor about hazards in time
Performance Criteria(PC) w.r.t. the Scope
Element Performance Criteria
Understanding of
potential sources of
accidents and
communicating
To be competent, the user/individual on the job must be able to:
PC1. avoid accidents related to use of potentially dangerous chemicals, gas torches,
sharp tools and hazards from machines
PC2. suggest process flow improvements to reduce anticipated or repetitive hazards
PC3. report mishandling of tools, machines or hazardous materials
PC4. identify electrical problems that could result in accident
PC5. spot and report potential hazards on time
PC6. follow company policy and rules regarding hazardous materials
PC7. deliver quality work on time as required by reporting any anticipated reasons
for delays
Knowledge and Understanding (K)
A. Organizational
Context
(Knowledge of the
company /
organization and
its processes)
The individual on the job needs to know and understand:
KA1. company’s policies on handling: harmful chemicals and sharp tools, safety and
hazards of machines, fire safety and, disposal of harmful chemicals and
materials
KA2. work flow involved in company’s jewellery manufacturing process
KA3. importance of the individual’s role in the workflow
KA4. reporting structure
B. Technical
Knowledge
The individual on the job needs to know and understand:
KB1. how different chemicals react and what could be the danger from them
KB2. how to use machines and tools without causing bodily harm
KB3. fire safety education
KB4. disposal of hazardous chemicals, tools and materials by following prescribed
environmental norms or as per company policy
Skills (S) [Optional]
A. Core Skills/
Generic Skills
Communication skills
The individual on the job needs to know and understand how:
SA1. to effectively communicate the danger
B. Professional Skills Decision making
The individual on the job needs to know and understand:
SB1. importance of reporting potential sources of danger
SB2. appropriate actions to be taken in the event of an accident
SB3. process for disposing of hazardous materials, safely and following
environmental guidelines
Reflective thinking
The individual on the job needs to know and understand how:
SB4. to learn from past mistakes regarding use of hazardous machines or
chemicals or gas torches
Critical thinking
The individual on the job needs to know and understand:
SB5. how to spot danger
SB6. procedures to follow in the event of a fire or other hazard
Keywords /Terms Description
Sector Sector is a conglomeration of different business operations having similar
business and interests. It may also be defined as a distinct subset of the
economy whose components share similar characteristics and interests.
Sub-sector Sub-sector is derived from a further breakdown based on the
characteristics and interests of its components.
Occupation Occupation is a set of job roles, which perform similar/ related set of
functions in an industry.
Function Function is an activity necessary for achieving the key purpose of the
sector, occupation, or an area of work, which can be carried out by a
person or a group of persons. Functions are identified through functional
analysis and form the basis of OS.
Sub-function Sub-functions are sub-activities essential to fulfil the achieving the
objectives of the function.
Job role Job role defines a unique set of functions that together form a unique
employment opportunity in an organisation.
Occupational Standards
(OS)
OS specify the standards of performance an individual must achieve
when carrying out a function in the workplace, together with the
knowledge and understanding they need to meet that standard
consistently. Occupational Standards are applicable both in the Indian
and global contexts.
Performance Criteria Performance criteria are statements that together specify the standard of
performance required when carrying out a task.
National Occupational
Standards (OS)
NOS are occupational standards which apply uniquely in the Indian
context.
Qualifications Pack (QP) QP comprises the set of OS, together with the educational, training and
other criteria required to perform a job role. A QP is assigned a unique
qualifications pack code.
Unit Code Unit code is a unique identifier for an Occupational Standard, which is
denoted by an ‘N’
Unit Title Unit title gives a clear overall statement about what the incumbent
should be able to do.
Description Description gives a short summary of the unit content. This would be
helpful to anyone searching on a database to verify that this is the
appropriate OS they are looking for.
Scope Scope is a set of statements specifying the range of variables that an
individual may have to deal with in carrying out the function which have
a critical impact on quality of performance required.
Knowledge and
Understanding
Knowledge and understanding are statements which together specify the
technical, generic, professional and organisational specific knowledge
that an individual needs in order to perform to the required standard.
Organisational Context Organisational context includes the way the organisation is structured
and how it operates, including the extent of operative knowledge
managers have of their relevant areas of responsibility.
Technical Knowledge Technical knowledge is the specific knowledge needed to accomplish
specific designated responsibilities.
Core Skills/ Generic
Skills
Core skills or generic skills are a group of skills that are the key to learning
and working in today’s world. These skills are typically needed in any
work environment in today’s world. These skills are typically needed in
any work environment. In the context of the OS, these include
communication related skills that are applicable to most job roles.
Keywords /Terms Description
IPR Intellectual Property Rights
NOS National Occupational Standard(s)
NVQF National Vocational Qualifications Framework
NSQF National Qualifications Framework
NVEQF National Vocational Education Qualifications Framework
QP Qualifications Pack
CRITERIA FOR ASSESSMENT OF TRAINEES
Job Role Goldsmith_Kundan-Jadau Jewellery
Qualification Pack Goldsmith_Kundan-Jadau Jewellery
Sector Skill Council GEMS & JEWELLERY
To pass the Assessment, a candidate needs to score 50% in Theory and 70% in Practical
Assessment Strategy Marks Allocation
NOS Elements Performance Criteria Theory Practical
- G&J/N0904 Make
components, frame,
Kundan (24K gold) and
Silver foils
Making components and
frame
PC1.make components of required dimensions such as size
and thickness 1 8
PC2.make components of required finish and evenness 1 8
PC3.draw or roll metal without overdrawing or splitting or
cracking 0 7
PC4.anneal the wire, strips and sheets for required
malleability for the thickness required 1 7
PC5.limit precious-metal loss of damaged metal rod or wire 1 7
PC6.accurately link the ends to form even rings, collets or
chains of required dimensions 1 7
PC7.link, solder and file the components into frame of
required finish and utility 0 5
PC8.achieve required flexibility, utility and symmetry of frame
as per design 1 4
PC9.meet productivity target 1 4
PC10.work with minimum hazards and accidents 1 4
Handling problems
PC11.deliver complete frames in time by reporting well in
advance, any problems faced or anticipated 0 2 - G&J/N0905 Engrave
pattern and apply
enamel
Engraving and enamel
painting
PC1.achieve symmetry of design to be engraved or etched for
applying enamel 0 2
PC2.achieve smooth finish of enamel paint as per design 0 1
PC3.ensure no overflow or excess enamel at the edges of the
painted area 0 1
PC4.ensure that enamel prepared with no impurities 0 1
PC5.ensure no chipping or cracking enamel 1 0
PC6.prepare surface of thickness and evenness for long term
enamel adhesion 1 0
PC7.fire at right temperature for the enamel to flow and set 1 0
PC8.achieve colour, vibrancy and gloss as per design 1 0
PC9.achieve hazard-free output after using acids and
chemicals 0 1