Basic Knowledge of Draping Dress
Draping is a foundational technique in fashion design that involves shaping and manipulating fabric directly on a dress form or mannequin to create garments. This class note explores the basic knowledge of draping dresses in fashion design, covering its importance, techniques, tools, types of fabric, practical applications, historical context, and contemporary relevance for aspiring designers looking to master this essential skill.

Importance of Draping in Fashion Design
Draping serves as a vital technique for fashion designers for several reasons:
- Creative Exploration: Allows designers to experiment with fabric, explore different shapes, and visualize garment silhouettes in three dimensions.
- Precision and Fit: Helps in achieving precise fit and drape of garments on the body, ensuring comfort and enhancing the aesthetic appeal.
- Design Development: Facilitates the translation of conceptual ideas into tangible garments, enabling designers to refine and perfect designs during the creative process.
- Problem Solving: Provides opportunities to address design challenges such as shaping complex curves, achieving balance in garment proportions, and integrating structural elements.
Techniques and Tools for Draping
1. Dress Form or Mannequin:
- Purpose: Essential tool for draping, providing a three-dimensional representation of the human body.
- Types: Available in various sizes, shapes (male, female, child), and materials (e.g., adjustable vs. fixed).
2. Fabric:
- Selection: Choose fabrics suitable for draping such as muslin, cotton, jersey, and silk, considering weight, drape, and stretch properties.
- Muslin: Preferred for initial draping trials due to its affordability and ability to hold pins and markings.

3. Draping Techniques:
- Pinning: Securing fabric on the dress form with pins to create desired shapes and silhouettes.
- Gathering and Pleating: Techniques for adding volume, texture, and detailing to garments.
- Manipulation: Folding, twisting, and tucking fabric to achieve desired folds and seams.
4. Marking and Tracing:
- Tools: Marking pencils, chalk, or fabric markers for tracing draping lines, seam allowances, and design details on fabric.
- Precision: Accurate marking ensures consistency and replicability in translating draped designs to flat pattern drafting.
5. Adjustments and Refinements:
- Fitting: Continual fitting and adjustment of draped fabric on the dress form to ensure proper fit and desired aesthetic.
- Iterative Process: Draping often involves multiple iterations and adjustments to perfect the design before finalizing patterns.
Types of Draping Techniques
1. Princess Draping:
- Description: Draping fabric to create a fitted bodice with vertical seams that follow the natural contours of the body.
- Applications: Dresses, blouses, and structured tops requiring precise fit and shaping.
2. Gathers and Ruching:
- Description: Gathering fabric to create soft folds and gathers, adding texture and volume to garments.
- Applications: Evening gowns, skirts, and dresses for special occasions.
3. Bias Draping:
- Description: Draping fabric on the bias (diagonal grain), creating fluid and drapey garments that cling to the body.
- Applications: Bias-cut dresses, skirts, and tops known for their flattering fit and movement.
4. Sculptural Draping:
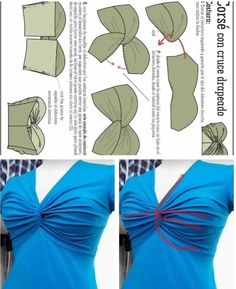
- Description: Manipulating fabric to create sculptural forms and shapes, often with exaggerated folds and asymmetry.
- Applications: Avant-garde fashion, couture garments, and experimental designs.
Practical Applications in Fashion Design
1. Couture and High Fashion:
- Customization: Draping used to create one-of-a-kind couture pieces tailored to individual clients.
- Innovation: Pushing creative boundaries with unique draping techniques and unconventional fabric manipulations.
2. Ready-to-Wear Collections:
- Prototyping: Draping for creating prototypes and samples before production, ensuring design integrity and fit.
- Efficiency: Streamlining the design process by visualizing and refining garment shapes directly on the dress form.
3. Pattern Development:
- Pattern Making: Translating draped designs into flat patterns for mass production, ensuring consistency and scalability.
- Collaboration: Collaborating with pattern makers and garment technologists to finalize patterns based on draped prototypes.
Historical Context and Contemporary Relevance
1. Historical Influence:
- Origins: Draping techniques have been used since ancient times, evolving with cultural and technological advancements in textile production.
- Haute Couture: Pioneered by couturiers like Charles Frederick Worth, Madame Grès, and Cristóbal Balenciaga, who elevated draping to an art form.
2. Contemporary Innovation:
- Technology: Integration of digital tools and software for virtual draping and 3D modeling, enhancing design visualization and efficiency.
- Sustainability: Sustainable draping practices using eco-friendly fabrics, waste reduction techniques, and ethical production methods.
Education and Skill Development

1. Fashion Design Programs:
- Curriculum: Incorporation of draping courses in fashion design programs, teaching students foundational techniques and advanced applications.
- Workshops and Masterclasses: Hands-on workshops and masterclasses with industry professionals to refine draping skills and explore new techniques.
2. Portfolio Development:
- Showcasing Skills: Including draping projects and illustrations in portfolios to demonstrate technical proficiency and creative vision.
- Industry Preparation: Preparing students for careers in fashion design, emphasizing the importance of draping in design studios and fashion houses.
Conclusion
Draping dresses in fashion design is an essential skill that combines artistry, technical proficiency, and creative expression. By mastering draping techniques, understanding fabric behavior, and refining design aesthetics, fashion designers can innovate and create garments that fit impeccably and convey their unique design vision. As fashion continues to evolve, draping remains a cornerstone of the design process, bridging tradition with innovation and shaping the future of fashion through craftsmanship and creativity.
