Model Ilustration Drawing
Fashion design relies heavily on visual communication, and one of the fundamental skills for any fashion designer is the ability to create accurate and expressive model illustrations. These drawings serve as the primary means of conveying design ideas, showcasing garments, and communicating the designer’s vision to clients, collaborators, and manufacturers.
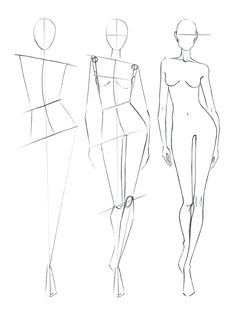
Model illustration drawing in fashion design involves capturing the essence of a garment on a stylized human figure. It combines elements of artistry, anatomy, and fashion knowledge to produce representations that are both aesthetically pleasing and informative. This class note aims to delve into the techniques, principles, and practices that underpin effective model illustration drawing in the context of fashion design.

Key Elements of Model Illustration Drawing
- Proportions and Anatomy:
- Understanding human proportions is crucial for creating realistic and appealing fashion illustrations. Fashion figures are typically elongated and stylized, with exaggerated proportions that emphasize the clothes rather than realism.
- Key proportions include elongated legs, a slender torso, and graceful necklines, which enhance the presentation of garments.
- Gesture and Movement:
- Fashion illustration should capture the dynamic essence of the garment through gesture and movement. The pose of the model influences how the clothing drapes and flows, conveying its fit and style.
- Gestural lines and fluid strokes help in suggesting movement and posture, making the illustration lively and engaging.
- Fashion Silhouettes:
- Silhouettes play a significant role in fashion design as they define the overall shape and outline of a garment. Fashion illustrators use silhouettes to highlight the unique characteristics of each piece of clothing.
- Silhouette variations (such as A-line, sheath, or fit-and-flare) are depicted through careful attention to the outline and volume of the garment.
- Fabric Rendering:
- The ability to render different fabrics convincingly adds depth and realism to fashion illustrations. Techniques such as shading, highlighting, and texture representation help in depicting the tactile qualities of materials like silk, wool, denim, and lace.
- Understanding how light interacts with different fabrics enhances the fidelity of the illustration and communicates the materiality of the garments effectively.
- Detailing and Embellishments:
- Details such as buttons, zippers, seams, and embellishments contribute to the authenticity and richness of fashion illustrations. They provide visual cues about the construction and design elements of the garment.
- Mastery of detailing involves precision in line work and a keen eye for capturing intricate design features that characterize each piece of clothing.
Techniques for Model Illustration Drawing
- Sketching and Drafting:
- Fashion illustrators often start with rough sketches to explore ideas and compositions. These initial drawings help in refining the concept before proceeding to more detailed illustrations.
- Drafting involves outlining the basic shapes and proportions of the figure and garment, establishing the foundation for the final illustration.
- Use of Templates and Croquis:
- Croquis (pre-drawn outline figures) serve as templates for fashion illustrations, providing a standardized base upon which designers can visualize their creations.
- Templates vary in poses and proportions, catering to different design requirements and styles. They streamline the illustration process and allow for consistency in figure representation.
- Color Application:
- Adding color to fashion illustrations enhances their visual impact and realism. Designers use markers, watercolors, digital tools, or mixed media to apply color and create vibrant compositions.
- Color choices reflect the mood, seasonality, and aesthetic of the collection, conveying additional layers of meaning beyond the garments themselves.
- Digital Illustration:
- In contemporary fashion design, digital tools such as graphic tablets and illustration software have revolutionized the illustration process.
- Digital platforms offer flexibility in editing, layering, and color manipulation, facilitating faster iterations and adjustments in response to client feedback or design changes.

Principles of Effective Fashion Illustration
- Expression and Style:
- Fashion illustration is a form of artistic expression that reflects the designer’s individual style and creativity. Developing a distinctive drawing style distinguishes designers and builds brand identity.
- Style choices encompass linework, shading techniques, use of color, and overall composition, contributing to the visual coherence of the illustrations.
- Composition and Balance:
- Composition refers to the arrangement of elements within an illustration. It involves balancing proportions, poses, negative space, and focal points to create a harmonious and visually compelling image.
- Attention to composition guides the viewer’s eye through the illustration, emphasizing key design features and conveying the intended narrative or theme.
- Narrative and Context:
- Fashion illustrations often tell a story or convey a specific mood or theme. The context of the illustration, such as the setting or occasion, influences stylistic choices and presentation.
- Narrative elements can include background details, accessories, and contextual cues that enhance the storytelling aspect of the illustration.
- Adaptability and Versatility:
- Fashion illustrators must adapt their style and techniques to suit different design briefs, client preferences, or target demographics.
- Versatility in illustration enables designers to communicate diverse fashion concepts—from haute couture to ready-to-wear—and cater to varying aesthetic sensibilities.
Applications and Career Pathways in Fashion Illustration
- Fashion Design Studios:
- Fashion houses and design studios employ illustrators to visualize and communicate design concepts to clients, pattern makers, and production teams.
- Illustrators collaborate closely with designers to translate sketches into prototypes and final garments, ensuring alignment with the original creative vision.
- Publishing and Editorial:
- Fashion illustrators contribute to fashion magazines, editorials, and online platforms, illustrating trends, runway looks, and seasonal collections.
- Editorial illustration requires the ability to capture the zeitgeist of fashion through expressive and timely visuals that resonate with readers.
- Advertising and Branding:
- Brands and advertising agencies utilize fashion illustration in marketing campaigns, advertisements, and promotional materials.
- Illustrators create compelling visuals that evoke brand identity, lifestyle aspirations, and consumer appeal, influencing purchasing decisions and brand perception.
- Freelance and Independent Practice:
- Many fashion illustrators pursue freelance careers, offering bespoke illustration services to individual clients, fashion startups, or online platforms.
- Freelancers leverage digital tools and social media to showcase their portfolios, build a client base, and establish a personal brand within the fashion illustration community.
Conclusion
Model illustration drawing is a cornerstone of fashion design, merging artistic skill with technical expertise to visually articulate clothing designs and concepts. Mastery of proportion, gesture, silhouette, fabric rendering, and detailing empowers fashion illustrators to convey creativity, innovation, and storytelling through their work.

Aspiring fashion designers and illustrators should cultivate a strong foundation in drawing techniques, explore diverse stylistic approaches, and embrace digital tools to remain adaptable and competitive in the dynamic fashion industry. By honing their craft and developing a distinctive artistic voice, fashion illustrators play a pivotal role in shaping trends, defining brand identities, and inspiring global audiences through the power of visual storytelling.
